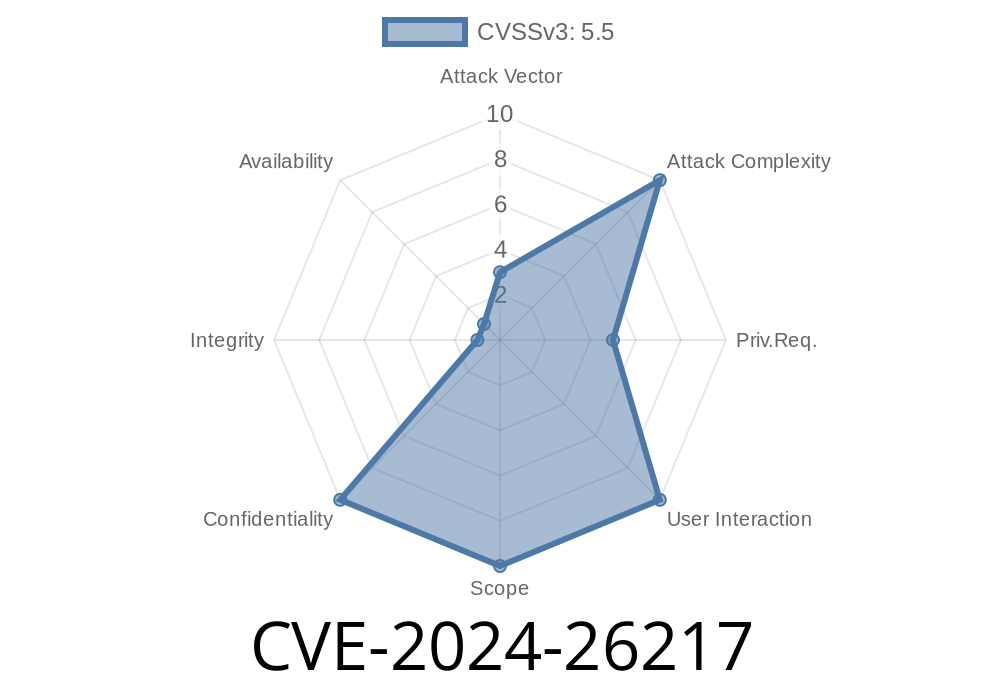
In March 2024, Microsoft patched a new vulnerability, CVE-2024-26217, in the Windows Remote Access Connection Manager (RasMan) service. This issue was rated "Important" and affects various supported versions of Windows. In this article, we’ll explain how this bug works in simple terms, what risks it poses, walk through a sample exploitation scenario, and provide resources for mitigation and further reading.
What is RasMan?
RasMan stands for Remote Access Connection Manager. It’s a Windows service responsible for handling dial-up and VPN connections. Many organizations rely on VPNs, so any flaw in this service could have a major impact.
Description of CVE-2024-26217
CVE-2024-26217 is an Information Disclosure Vulnerability. This means that an attacker can learn information they shouldn’t have access to—a key step in many attacks.
According to Microsoft’s advisory:
> "This vulnerability allows a local attacker to gain information that could be useful for further compromise. Exploitation requires the attacker to log on to the system and run a specially crafted application."
Affected Systems:
How Does the Vulnerability Work?
Because RasMan operates with high privileges, if malicious users can trick it into leaking sensitive data (like pieces of computer memory containing passwords, system tokens, or credentials), they can potentially escalate their own privileges or start lateral movement.
In this case, the vulnerability comes from the way RasMan improperly manages memory. Attackers can interact with it via its RPC (Remote Procedure Call) interface.
Example Code Snippet
Below is a very simple demonstration of querying the RasMan service. This is NOT an exploit, but it sets the stage for how attackers might interact with RasMan:
import win32com.client
rasman = win32com.client.Dispatch("RasAuto")
try:
# Attempt to call a RasMan method
status = rasman.GetAutoDialParam()
print("RasMan Response: ", status)
except Exception as e:
print("Error communicating with RasMan:", e)
An actual exploit would involve sending malformed RPC requests, potentially using C/C++ and complicated Win32 API calls, or leveraging custom RPC clients to interact with undocumented RasMan functions.
For advanced readers, the open-source Impacket toolkit is often used to create RPC calls on Windows.
Mitigation and Detection
Patch your systems. Microsoft released fixes as part of March 2024 Patch Tuesday. Always prioritize updating!
Monitor for suspicious RasMan usage: Look for non-standard usage patterns from non-administrator accounts.
Restrict local access: Least-privilege practices limit the damage an attacker can do if they get access.
Useful References
- Microsoft Advisory CVE-2024-26217
- NVD CVE-2024-26217 Entry
- What is RasMan?
- Impacket toolkit for RPC work
Conclusion
CVE-2024-26217 is a great reminder that even niche Windows components like RasMan can contain critical bugs. While exploitation is limited to local attackers, the information that could be leaked might be just the foothold an adversary needs.
Patch regularly, follow least-privilege guidelines, and stay informed about these "low-hanging fruit" vulnerabilities—they’re often used by real attackers as part of broader attacks.
If you want more details or a walkthrough of real exploitation code, stay tuned to security research blogs as more technical write-ups emerge!
Timeline
Published on: 04/09/2024 17:15:40 UTC
Last modified on: 04/10/2024 13:24:00 UTC