Published: June 2024
Affected: Linux kernel (nouveau driver)
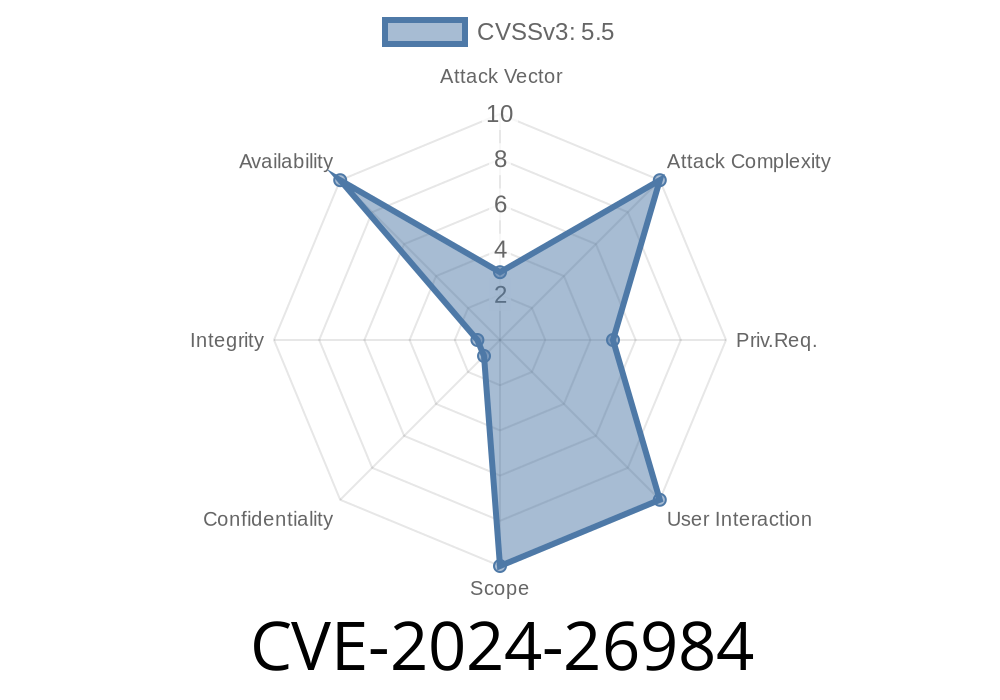
Severity: High
References:
- Upstream Kernel commit fixing bug
- CVSS details and NVD entry
The Linux kernel Nouveau driver for NVIDIA GPUs recently fixed a subtle, high-severity race condition in its memory management routines (CVE-2024-26984). If you run graphics or compute workloads—especially with parallel Vulkan CTS—on affected kernels, this bug _could_ cause system instability, kernel panics, or enable potential denial-of-service attacks. We'll break down what happened, show a code example, and outline how a malicious user could trigger (and why they can’t easily exploit further).
What’s the Vulnerability?
Summary:
A _race condition_ existed in how the Nouveau driver managed memory ("instmem") pointers for GPU page tables. In rare conditions, two threads could simultaneously acquire the same GPU resource. The reference counter (refcount_set and refcount_inc_not_zero) could increment so one thread used the resource before an internal pointer (ptrs) was actually visible to the other—in effect, Thread B saw a NULL where it shouldn’t.
This manifested *only* with intense parallel operations, like running thousands of Vulkan tests or stress-testing deep into the Nouveau code.
Example Kernel Crash
BUG: kernel NULL pointer dereference, address: 0000000000000008
...
RIP: 001:gp100_vmm_pgt_mem+xe3/x180 [nouveau]
...
Every so often pt->memory->ptrs is NULL.
This ptrs ptr is set in nv50_instobj_acquire called from nvkm_kmap.
Technical Background – The Race
Suppose Thread A and Thread B both call nv50_instobj_acquire() for the same physical GPU memory area:
Thread A sets the refcount (refcount_set).
2. Thread B, almost simultaneously, increases it (refcount_inc_not_zero) and gets a pointer to the object.
3. Thread B now uses the object _before_ Thread A finished completely setting up the ptrs field due to missing memory barrier; it can see a bogus or NULL value, leading to a crash.
This happens because memory writes by Thread A aren't forcibly made visible before other cores read them. This is a classic example of a synchronization flaw in SMP (multicore) environments.
The Fix: Enforced Memory Barriers
To make sure no CPU sees half-initialized objects, the patch adds explicit memory barriers.
Before (vulnerable)
refcount_set(&obj->refcount, 1);
obj->ptrs = whatever; // not guaranteed that other CPUs will see this update before refcount change
After (fixed)
refcount_set(&obj->refcount, 1);
smp_wmb(); // Ensure the pointer store is visible before anyone else gets the object
obj->ptrs = whatever;
Additionally, places that read ptrs use paired smp_rmb() to enforce ordering.
1. Denial of Service (DoS):
- A regular user with access to GPU compute can deliberately run many parallel mappings/unmappings, or craft a program to exploit the race, eventually causing a kernel crash (NULL dereference).
- Exploiting for code execution looks very unlikely due to the NULL nature of the pointer and lack of attacker control.
If you want to stress/test for the bug (on a vulnerable kernel)
// Not full exploit but simulates bug condition -- use with caution!
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define NUM_THREADS 64
void* stress_nouveau(void* arg) {
while (1) {
// Could use DRM/ioctl calls to trigger mapping/unmapping
// For demo: see deqp-vk or similar tools for real stress
system("vkcube --present ");
}
return NULL;
}
int main() {
pthread_t threads[NUM_THREADS];
for(int i=; i<NUM_THREADS; i++)
pthread_create(&threads[i], NULL, stress_nouveau, NULL);
for(int i=; i<NUM_THREADS; i++)
pthread_join(threads[i], NULL);
return ;
}
Note: Running something similar on patched kernels _will not_ reproduce the issue.
Local user with GPU access (not remote).
- On systems using Nouveau and running a vulnerable kernel (most notably between ~late 2022 – early 2024, kernel 6.5–6.8).
Impact and Mitigation
- Kernel crash/ DoS: Potential for system instability or halt (requires reboot).
No privilege escalation: The bug is not known to grant root or leak data directly.
- Patched in: Linux kernel mainline as of this commit in March 2024.
Upstream kernel discussion and patch:
nouveau: fix instmem race condition around ptr stores
CVE database:
Similar bug reports:
Red Hat Bugzilla #2261915 (example downstream)
Conclusion
CVE-2024-26984 is a prime example of how tricky kernel-level race conditions can cause rare, hard-to-reproduce system crashes, often surfacing only with heavy concurrent workloads. You should update your kernel ASAP if you use Nouveau anywhere in production or allow regular users GPU access.
The fix—careful memory ordering using explicit barriers—makes this class of bug much less likely. Thanks to kernel developers for catching and patching this before widespread exploitation.
Timeline
Published on: 05/01/2024 06:15:15 UTC
Last modified on: 07/03/2024 01:50:12 UTC