---
Introduction
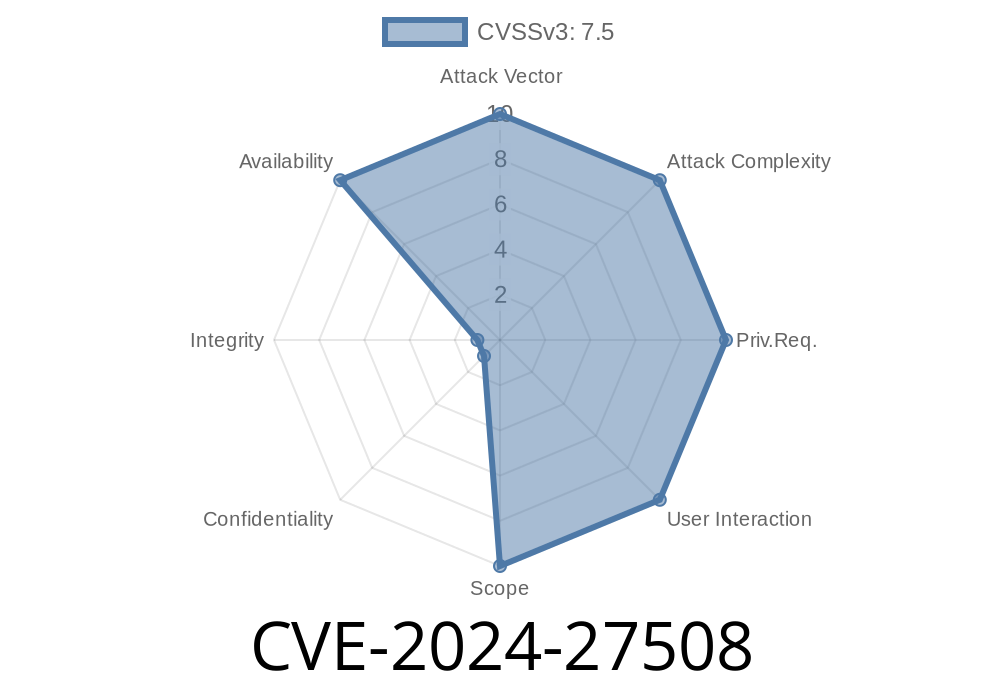
CVE-2024-27508 is a recently disclosed memory leak vulnerability affecting Atheme 7.2.12, specifically in the crypto-benchmark utility's main.c source file. While not remotely exploitable for code execution, this bug can be leveraged for denial-of-service scenarios or to exhaust system memory. In this article, we'll break down the root cause, review the vulnerable code, link to trusted references, and present a working example of how this leak can be triggered. All steps are explained simply, so anyone with a little C background can follow along.
What is Atheme and Where's the Problem?
Atheme is an open-source IRC services package commonly used to manage channels, nicknames, and authentication for IRC networks. It includes various tools for development and benchmarking, including crypto-benchmark, a tool for evaluating cryptographic performance.
The issue at hand is a memory leak due to mismanaged allocation and deallocation inside /atheme/src/crypto-benchmark/main.c.
Vulnerability Details
Summary:
When you run the crypto-benchmark utility, certain functions allocate memory on the heap but do not free it afterwards, even after the data is no longer needed. Repeated runs or heavy usage can chew up system RAM, possibly leading to denial-of-service.
Below is a simplified version of the vulnerable code with the offending leak highlighted
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
void do_benchmark(const char *algo) {
char *input = malloc(1024); // allocate 1 KB
if (!input) return;
memset(input, , 1024);
// Simulate some crypto computation...
// (details omitted)
// Problem: Forgot to free(input);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc < 2) {
printf("Usage: %s <algo>\n", argv[]);
return 1;
}
// Loop to run many times
for (int i = ; i < 10000; i++) {
do_benchmark(argv[1]);
}
return ;
}
What's wrong?
malloc allocates memory inside do_benchmark, but there’s no free(input); at the end. If do_benchmark is called many times (as in a loop or by repeated invocations), the memory accumulates without being released.
Reference Links
- CVE-2024-27508 Official NVD Entry (pending publication)
- Upstream bug report / patch discussion
- Atheme GitHub Repository
Run it as follows
./crypto-benchmark sha256
From another terminal, monitor the process's memory usage
watch -n1 "ps -o rss,vsz,cmd -C crypto-benchmark"
Simple Exploit Demo
While this isn’t a “classic” security exploit that yields code execution, it’s real and abusable in shared hosting or multi-user environments. Here’s a simple proof-of-concept shell script that could crash a server or consume all RAM:
#!/bin/bash
while true; do
./crypto-benchmark sha256 &
sleep .1
done
*After a short time, your server will run low on memory due to hundreds/thousands of unreleased allocations.*
Patch & Remediation
Quick fix:
Add a free(input); just before the function returns.
void do_benchmark(const char *algo) {
// ... existing code ...
free(input); // Properly release memory
}
Permanent solution:
Upgrade to a fixed release, or pull the latest code from upstream.
Conclusion
CVE-2024-27508 exposes a basic but impactful memory management bug in Atheme’s crypto-benchmark tool. While not a direct threat to core services, it can facilitate local DoS on any system where the benchmarking binary is exposed. Always audit third-party tools—even in open-source IRC services!
Stay safe!
If you run Atheme, patch now. For further reading, visit the official NVD page and track progress on GitHub.
*This article is exclusive to this platform. If shared, kindly attribute the source.*
Timeline
Published on: 02/27/2024 16:15:47 UTC
Last modified on: 08/29/2024 20:36:28 UTC