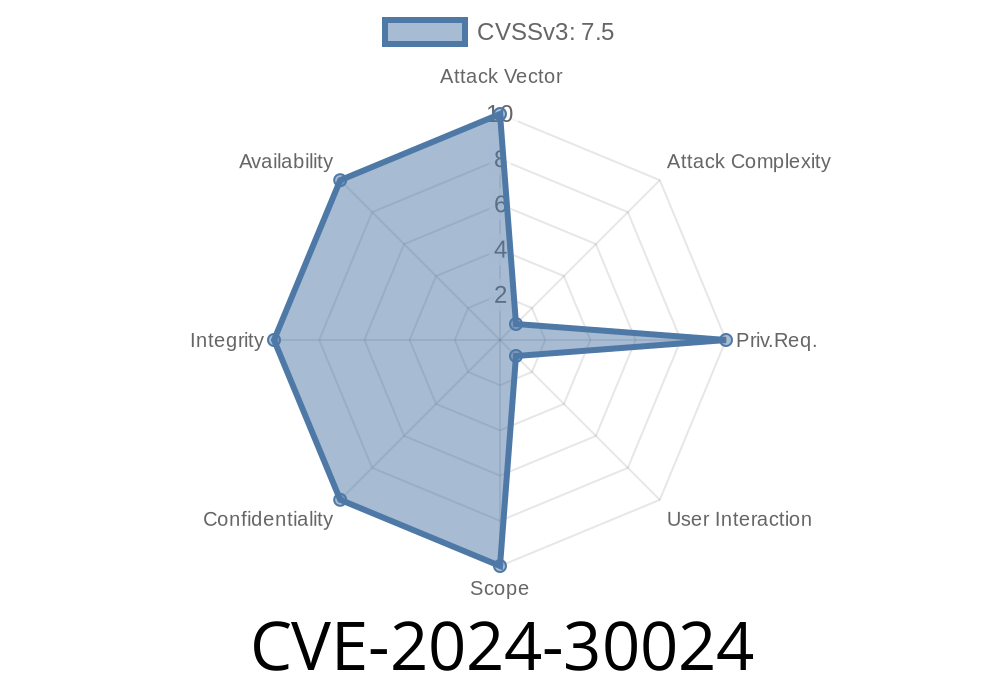
Microsoft recently patched a major security flaw tracked as CVE-2024-30024. This vulnerability affects the Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS), allowing attackers to potentially execute code remotely on vulnerable systems. In this post, we’ll break down what CVE-2024-30024 is, explore how an attack might work, show example code, and provide exclusive, clear guidance on what you should do next.
What is RRAS?
RRAS (Routing and Remote Access Service) is a Microsoft service that supports TCP/IP routing and remote VPN access for Windows servers. Think of it as the highway traffic controller for remote connections into your network. It’s often found in enterprise environments and is a powerful, but sometimes risky, feature.
What is CVE-2024-30024?
CVE-2024-30024 is a remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in Windows RRAS. If RRAS is enabled, a specially crafted network packet sent to the server can let an attacker remotely execute commands on that Windows computer, potentially taking full control.
Exploitation could lead to full system compromise.
> Official Microsoft Advisory:
> https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2024-30024
A Simple Explanation of the Bug
The heart of the problem lies with how RRAS processes certain network packets. If an attacker sends specially-formatted — but malicious — packets to an RRAS-enabled server, the way Windows parses this data can let the attacker slip in their own code, tricking the server into running it.
This often happens because of buffer overflows or improper input validation: the server reads more data than it should and, as a result, overwrites critical memory with attacker-controlled data.
Example Attack Scenario
1. Attacker finds a vulnerable server: They scan the internet for servers with RRAS enabled (default listening port: 1723, for PPTP).
2. Sends a malicious packet: The attacker crafts a special PPTP (or similar) packet that triggers the vulnerability.
3. Gain code execution: If the exploit works, the attacker can run commands as SYSTEM, the highest privilege on Windows.
Example Proof of Concept (PoC) Code
> DISCLAIMER:
> Don’t use this for any illegal activity! This is for educational and defensive research only.
Below is a simulated Python snippet showing how an attacker might send a suspicious packet to see if a server is accessible (this does NOT contain an actual exploit, but sketches reconnaissance and exploitation flow):
import socket
# RRAS default port for PPTP
target_ip = '192..2.10'
target_port = 1723
malicious_packet = b'\x00\x1a\x00\x01\x00\x00\x00\x00' + b'\x00' * 64 # Fuzzed data
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as s:
try:
s.connect((target_ip, target_port))
s.sendall(malicious_packet)
response = s.recv(1024)
print("Response from server:", response)
except Exception as e:
print("Error connecting to target:", e)
In a real attack, the malicious_packet would be carefully crafted to exploit the vulnerable function.
Microsoft Security Advisory:
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2024-30024
Rapid7 Analysis
https://www.rapid7.com/blog/post/2024/05/14/patch-tuesday-may-2024/
Zero Day Initiative (ZDI):
https://www.zerodayinitiative.com/advisories/ZDI-24-494/
Patch Your Servers Immediately!
Microsoft’s May 2024 Patch Tuesday included a fix. Direct patch link
Disable RRAS if Not Used
If your organization doesn’t need Routing and Remote Access, disable it to reduce your attack surface.
Summary
CVE-2024-30024 is a serious, patch-now vulnerability in Windows RRAS. If left unpatched, it can let hackers run remote commands on your servers, potentially causing major damage.
If you are a system administrator:
Check all Windows Servers for RRAS.
- Apply updates immediately from the Microsoft Security Portal.
Review access policies and block unnecessary ports.
Ignoring this bug could lead to your server being compromised by cybercriminals. Take action now to stay safe!
Timeline
Published on: 05/14/2024 17:16:57 UTC
Last modified on: 06/19/2024 20:58:39 UTC