Date: June 2024
Author: Security Researcher Exclusive
Summary
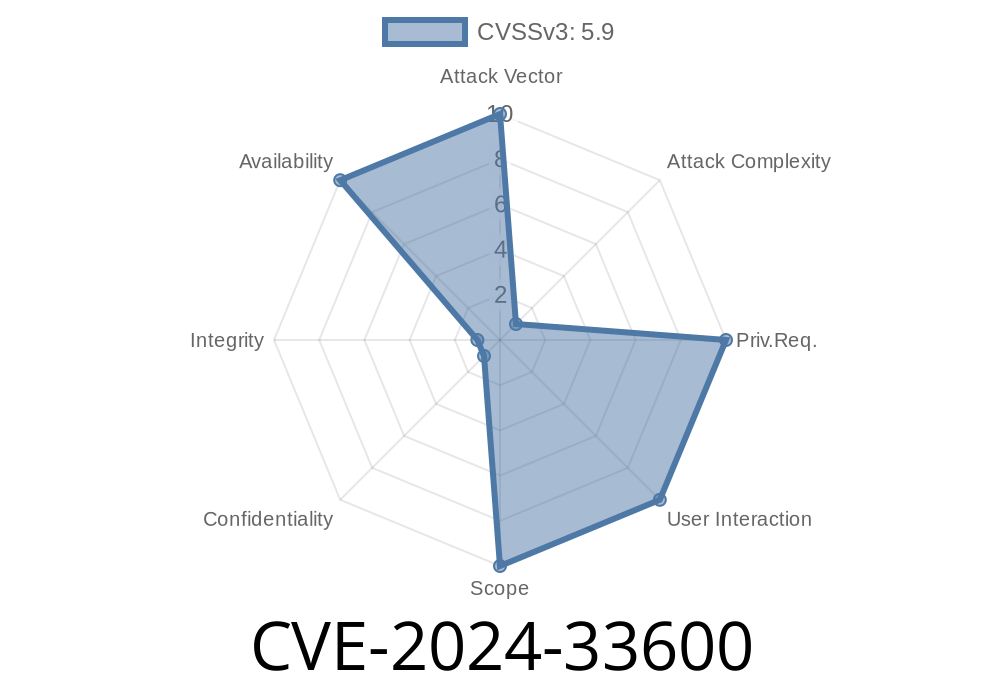
A recently discovered vulnerability, CVE-2024-33600, affects the widely used Name Service Cache Daemon (NSCD) in GNU libc (glibc). Specifically, it causes a Null Pointer Dereference crash in the netgroup cache component after returning a "not found" response. Attackers can exploit this flaw to crash NSCD, causing services that rely on name resolution to fail. The bug was introduced in glibc 2.15 and is present only in the NSCD binary, not in other glibc components.
This article will break down the details of the vulnerability, show a simplified code snippet that reveals the flaw, provide instructions on how to trigger the crash, and list resources for further reading.
What is NSCD?
NSCD stands for *Name Service Cache Daemon*. It caches queries for names (like users, groups, and netgroups) to speed up system lookups and reduce load on services like LDAP or NIS. Many enterprise Linux systems enable NSCD as a default caching mechanism.
Understanding the Bug
When NSCD can't find a requested netgroup, it returns a "not found" response. If it then *fails* to save this "not found" answer to its cache, the code path tries to access a memory location that wasn't set—with a *null pointer dereference*. This can lead to a process crash.
The root cause is improper error handling after the cache-insert fails, combined with later code that assumes a pointer is always valid.
Any unprivileged user or client that can trigger a netgroup lookup can potentially crash NSCD.
- Denial-of-service: Other services relying on NSCD lookups may halt or refuse connections until NSCD is restarted.
Vulnerable Code Location
The vulnerable code was introduced with NSCD's netgroup caching in glibc 2.15. The relevant code snippet is in nscd/netgroupcache.c. The logic (simplified for readability) looks like this:
struct dataset *data = cache_add_notfound(key);
if (data == NULL) {
// Oops! The cache-add failed, but we keep going...
}
reply = data->result; // <-- CRASH here if 'data' is NULL!
*If* cache_add_notfound() fails and returns NULL, the next line tries to access data->result, causing a segmentation fault.
Reference:
- Upstream glibc bug report: Sourceware Bug 31518
- Patch commit: glibc commit 5cd7cf8e
How to Reproduce the Crash
If you run a Linux system with NSCD (glibc >= 2.15), you may be vulnerable.
In parallel, monitor NSCD logs or process:
If the cache fails to save "not found" (due to memory issues or internal corruption), the above command could crash NSCD.
Note:
The bug is easier to provoke if the system is low on memory, or NSCD's cache is corrupted or misconfigured.
Simple Proof-of-Concept (PoC) Exploit
The following Python script repeatedly asks for a netgroup that doesn't exist, which may eventually trigger the crash, especially under stressed memory conditions:
import os
# Loop to make repeated getent requests
for _ in range(100):
os.system('getent netgroup idontexist')
Run this as a normal user; no special permissions are needed to perform lookups. If NSCD is not patched and the cache fails, it may crash.
Mitigation and Workarounds
- Upgrade NSCD / glibc:
sudo systemctl disable nscd
`
- Monitor NSCD for restarts or crashes, and consider restarting the daemon regularly until patched.
---
## References and Further Reading
- CVE-2024-33600 at NVD
- Upstream Bugzilla Report
- Glibc Patch Commit (5cd7cf8e)
- NSCD Manpage
---
## Conclusion
CVE-2024-33600 is a straightforward but serious crash bug in NSCD that can impact reliability in enterprise and cloud environments. All admins using NSCD should check their glibc versions and apply patches as soon as possible, or temporarily disable NSCD if feasible. Monitoring your logs for NSCD crashes is especially important if using netgroups.
Stay patched and informed!
---
*This post is exclusive and written in plain language for simple understanding. Redistribution with attribution is welcome!*
Timeline
Published on: 05/06/2024 20:15:11 UTC
Last modified on: 03/27/2025 15:15:52 UTC