---
1. Introduction
Another day, another serious security flaw. In June 2024, Microsoft patched a dangerous bug now tracked as CVE-2024-49106. In simple terms, this is a Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability in the Windows Remote Desktop Services (RDS). If a hacker knows how, they could take control of your system remotely, just by connecting to it in a certain way. Let's break down what this means, who should worry, and what you can do about it.
2. What is CVE-2024-49106?
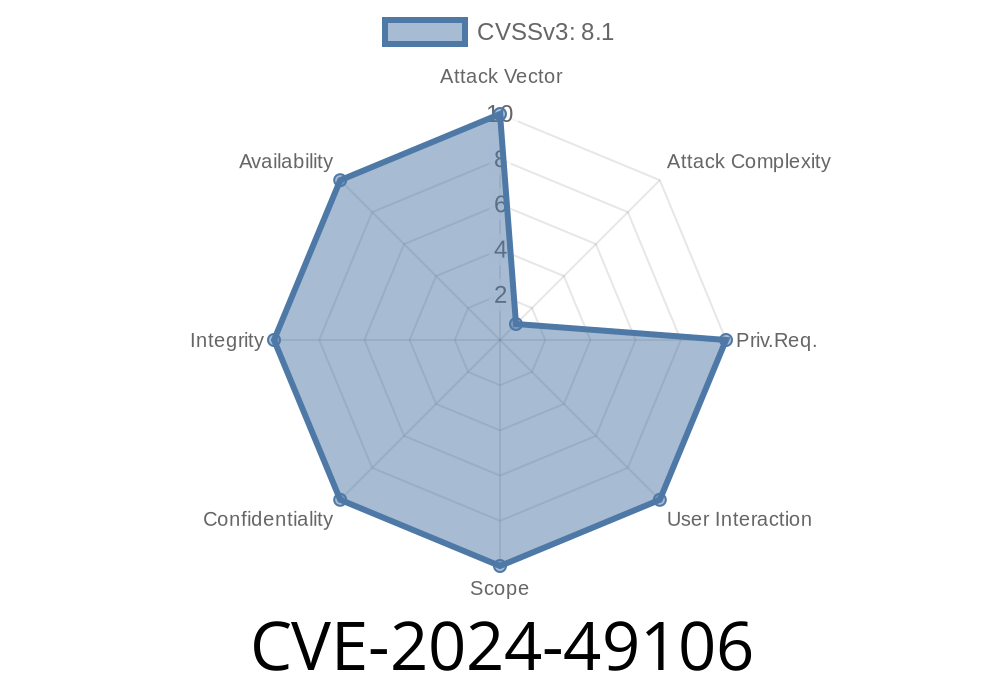
CVE-2024-49106 is a security vulnerability in *Remote Desktop Services* (formerly known as Terminal Services) across multiple supported Windows versions. This bug allows an unauthenticated attacker—someone who doesn’t even need a username or password—to run code on a remote computer just by sending specially crafted data during RDP session negotiation.
This could let the attacker install programs, view or change data, or create new accounts with full user rights. In the hands of ransomware attackers, this is scary stuff.
The Flaw
When a client connects to a Windows computer using RDS, there is a handshake process where the two computers negotiate settings. CVE-2024-49106 is a heap-based buffer overflow in this process. If an attacker sends a malicious packet during the negotiation, they can overflow the buffer and execute code of their choice.
User Interaction: None
> *Basically, if your computer is listening for RDP connections, it’s at risk.*
Anyone who
- Exposes Windows RDS (RDP, TCP/3389) to the internet or untrusted networks
Does not have the June 2024 security update installed
*Ransomware groups and network worms love these kinds of issues.*
5. Proof-of-Concept (PoC) Exploit
Below is a simplified pseudo-code example that demonstrates how the exploit might look. (Do not use this for illegal purposes, for educational only!)
import socket
def send_malicious_rdp_packet(target_ip, port=3389):
# This is a placeholder. Real exploit data would be crafted here
malicious_packet = b'\x03\x00\x00\x13' + b'\xAA' * 1024 # Overflow the buffer
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect((target_ip, port))
s.send(malicious_packet)
print(f"Sent malicious packet to {target_ip}:{port}")
s.close()
# Example usage
send_malicious_rdp_packet("192.168.1.10")
*The actual exploit is more complex, but the key is sending a specially crafted packet to the target's RDP port (3389/tcp) to crash or take over the service.*
What You Should Do
1. Update Now: Install Microsoft’s June 2024 security patches.
2. Block RDP where possible: Don’t expose port 3389 to the internet. Use VPN or restrict by firewall.
Microsoft’s CVE Bulletin:
CVE-2024-49106 on MSRC
- US-CERT Alert
- Microsoft Remote Desktop Services Documentation
Final Words
CVE-2024-49106 is critical. If you manage Windows servers or workstations and use Remote Desktop, patch asap. Vulnerabilities like this are highly sought after by cybercriminals. Don’t wait until it’s too late—update and secure your networks.
Timeline
Published on: 12/12/2024 02:04:36 UTC
Last modified on: 12/19/2024 17:45:14 UTC