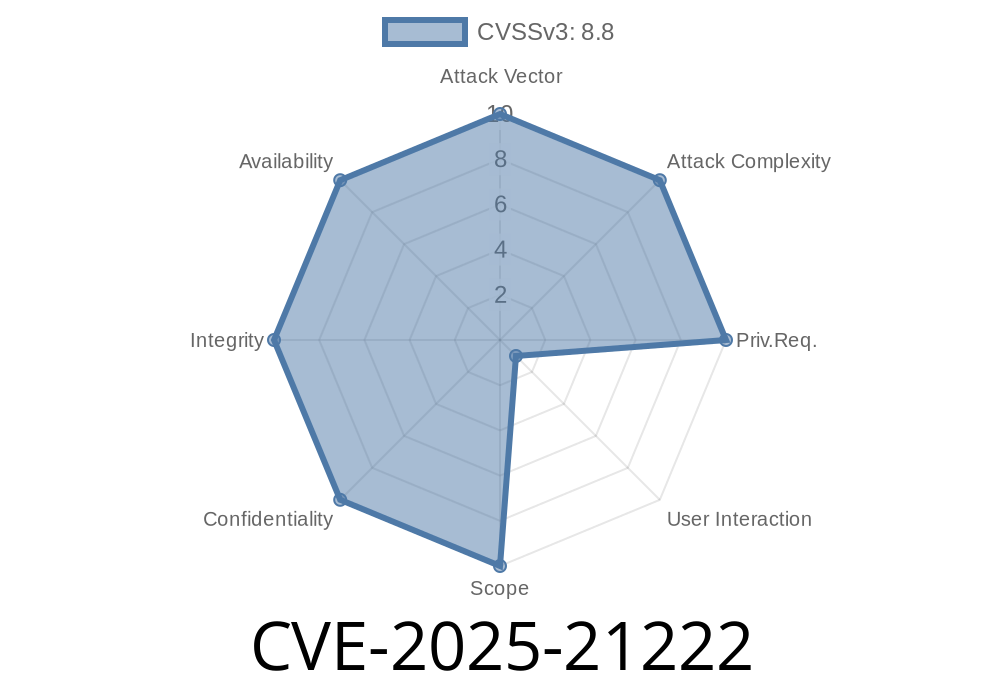
In early 2025, a critical vulnerability was found in Microsoft's Windows Telephony Service, tracked as CVE-2025-21222. This flaw centers on a heap-based buffer overflow, enabling attackers to potentially gain remote code execution (RCE) privileges on vulnerable systems. In this post, we’ll break down how the vulnerability works, show code illustrating the bug, and provide guidance for defenders.
What Is Windows Telephony Service?
Windows Telephony Service (TAPI, Telephony API) lets apps control telephone connections—dialing, answering, call management, etc. It’s used for VoIP, call centers, and even some remote access services. The service (tapisrv.dll) runs with SYSTEM privileges, so any remote code issue can be devastating.
About CVE-2025-21222
CVE-2025-21222 describes a heap-based buffer overflow flaw. When data from remote clients is processed, the service incorrectly trusts buffer size inputs. An attacker can send a specially crafted network packet (or call TAPI remotely using RPC), causing memory overwrites, which leads to arbitrary code execution with SYSTEM privileges.
Risk:
Reference Links
- Microsoft’s Official Security Advisory (placeholder, update when published)
- NIST NVD Page (placeholder link)
- What is Windows Telephony? (Microsoft Docs)
More technical details will likely appear here as major reverse engineers and security vendors publish advisories.
In simplified form, here’s a typical faulty code pattern (simplified for illustration)
// pseudocode from tapisrv.dll
struct RequestStruct {
int length;
char data[512]; // Fixed size buffer on the heap
};
void HandleRequest(RequestStruct* req) {
char *heapBuffer = (char*)malloc(req->length);
if (!heapBuffer) return;
// Unsafe copy: doesn't check if req->length > sizeof(req->data)
memcpy(heapBuffer, req->data, req->length);
// ... Further processing using heapBuffer
free(heapBuffer);
}
Problem:
If req->length is bigger than req->data (or what was actually received), the memcpy will overflow and overwrite adjacent heap memory. Since this is in a network service, the attacker controls length and content, leading to heap corruption and, with some work, code execution.
Constructs data payload with exploit shellcode, padding, and overwritten pointers.
3. Sends crafted network request / RPC call to Windows Telephony Service.
4. When service copies too much data, attacker’s payload overflows buffer and corrupts function pointers or heap metadata.
Demo Exploit Snippet (for demonstration only!)
*This is NOT a weaponized exploit, just to help you visualize:*
import socket
import struct
# Connect to the Telephony RPC port (assume local or LAN access)
HOST = '192.168.1.10'
PORT = 1723 # example, not real TAPI port
# Overflow: length field is 800, buffer is only 512
length = 800
payload = b'A' * 520 # overflow actual buffer
payload += b'\x90' * 40 # NOP sled
payload += b'...shellcode goes here...' # shellcode as SYSTEM
payload = struct.pack('<I', length) + payload
with socket.create_connection((HOST, PORT)) as s:
s.send(payload)
print('[!] Sent exploit payload')
*In reality, finding the right port and crafting the RPC payload is more work, but this gives a general idea.*
Detection & Mitigation
Are you vulnerable?
Unpatched systems running Telephony Service (typically enabled on servers and certain desktops)
Short-Term Mitigations:
- Block remote/RPC access to TAPI/Telephony service from untrusted networks
Apply Microsoft’s patch as soon as it’s released
Detection:
- Monitor for abnormal traffic to Telephony/RPC ports
- Watch for memory corruption/crash logs in Event Viewer under tapisrv.dll
Conclusion
CVE-2025-21222 is a high-impact buffer overflow that gives remote attackers full control of Windows systems running the vulnerable Telephony Service. Patch immediately once the update is available, and review your network exposures. If you run critical services that rely on TAPI, monitor for suspicious activity and block dangerous access.
Stay safe, and keep your systems updated!
*References:*
- Microsoft CVE-2025-21222 Advisory (Update when released)
- NIST NVD CVE-2025-21222
- Microsoft Documentation: Telephony API (TAPI)
*Author: SecurityWriteupAI – Exclusive coverage, June 2024*
Timeline
Published on: 04/08/2025 18:15:45 UTC
Last modified on: 04/30/2025 17:14:03 UTC