In April 2025, Oracle disclosed a high-severity security vulnerability (CVE-2025-21587) in its Oracle Java SE and GraalVM product lines. This article will break down what the vulnerability is, why it matters, how exploitation works, and what code and remediation look like. I’ll keep things clear and actionable for Java developers, sysadmins, and security teams.
What Is CVE-2025-21587?
CVE-2025-21587 is a vulnerability in the JSSE (Java Secure Socket Extension) component within the following Oracle products:
Oracle GraalVM Enterprise Edition: 20.3.17, 21.3.13
This vulnerability allows a remote, unauthenticated attacker to compromise Java and GraalVM-based systems via various protocols, leading to:
Breach of data integrity
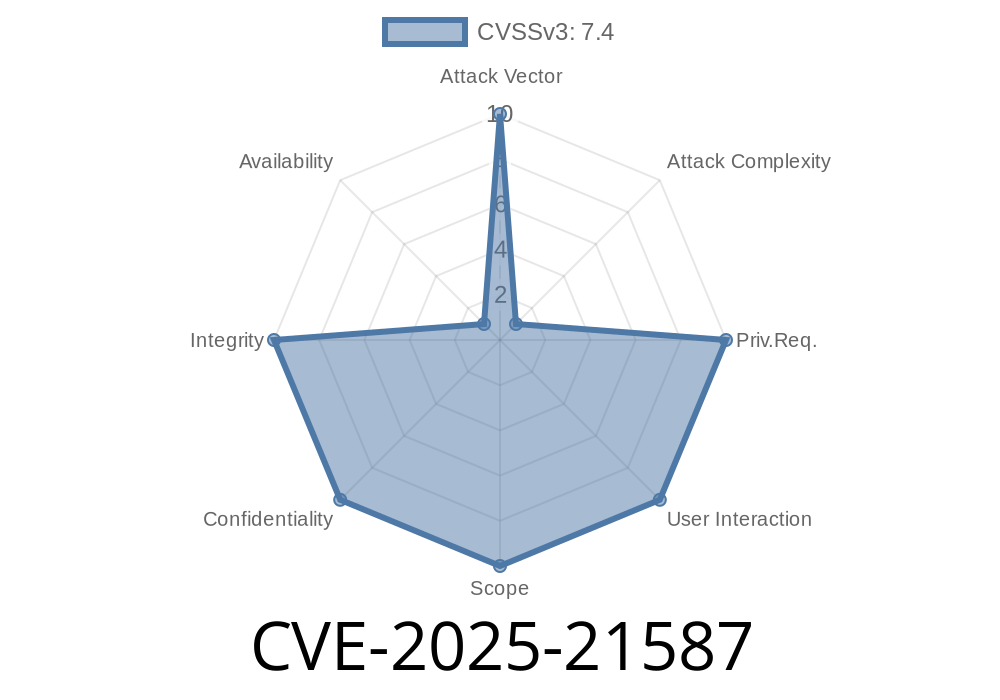
CVSS 3.1 base score: 7.4 (High)
*Vector: (CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:H/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:N)*
Why Does This Matter?
- Wide Impact: Affects standard Java, GraalVM, and even sandboxed applet/Web Start environments.
- Network Exploitable: Can be triggered remotely, needing only network access—no credentials required.
- Data Focused: Allows full read/write to application data, with no impact to availability (A:N).
Technical Details
Oracle has not published full PoC (Proof-of-Concept) code or exploitation samples as of this writing, but the vulnerability lies in the handling of input to the JSSE APIs. Web services supplying improper or malicious data to the JSSE APIs can trigger the issue.
The JSSE subsystem, which is used for SSL/TLS processing and secure communication, fails to correctly validate or sanitize specific forms of input—making data accessible or modifiable due to an improperly enforced boundary check.
Exploit Scenario
> Let’s imagine a Java application exposes a web service that allows users to upload or download files securely using HTTPS. Internally, it uses JSSE APIs to negotiate the connection and process requests.
Use a protocol (like HTTPS) supported by the service.
- Inject data or commands that would bypass normal access controls, allowing unauthorized modifications or exfiltration of business-critical data.
Below is a conceptual example (not an official PoC)
// Vulnerable: Accepts remote data and initializes SSLContext directly
public void processClientRequest(byte[] clientInput) {
try {
// Potentially untrusted input sent over a web service/API
SSLContext sslContext = SSLContext.getInstance("TLS");
// Attacker can provide manipulated KeyManagers or TrustManagers via input
sslContext.init(getKeyManagers(clientInput), getTrustManagers(clientInput), null);
// ... continue processing using sslContext ...
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle exception
}
}
// Instead, use only trusted configurations!
The attacker’s goal:
Pass crafted data as clientInput to trigger the vulnerability, gaining control over the SSL/TLS negotiation, and thereby accessing or modifying sensitive data.
Check your Java version
java -version
GraalVM EE 20.3.17, 21.3.13
If you’re running any product/version above, you are at risk unless you’ve applied the latest Oracle Critical Patch Update (CPU).
High attack complexity (some knowledge of protocols and API specifics needed)
- Can be triggered via web services, sandboxed client-side Java (applet or Web Start) that processes untrusted code from the internet
Payload is processed by a service using vulnerable JSSE methods.
- Insufficient validation in JSSE allows attacker to read/write arbitrary data, potentially escalate privileges.
How to Fix
- Apply Patch Immediately: Visit Oracle’s official advisory and apply the latest updates for your product version.
Oracle Critical Patch Update Advisory - April 2025
Restrict Network Access: Shield vulnerable services behind firewalls or VPNs until patched.
- Input Sanitization: Never pass untrusted data directly into security-sensitive Java APIs, like SSLContext or Key/TrustManager constructors.
References
- Oracle Advisory - CVE-2025-21587
- NVD Entry for CVE-2025-21587 _(Check for updates as public details emerge)_
- JSSE Documentation
TL;DR
- CVE-2025-21587 affects Oracle Java SE and GraalVM’s SSL/TLS subsystem (JSSE).
- Remote attackers can exploit the vulnerability without authentication to access/modify application data.
- Apply the latest Oracle patch as soon as possible and review your use of JSSE with untrusted data sources.
Public exploit code is not yet widespread, but due to the impact, resolution is critical.
Stay safe! Patch now and audit your Java-based services for any use of untrusted input in security or cryptography APIs.
Timeline
Published on: 04/15/2025 21:15:54 UTC
Last modified on: 04/16/2025 16:15:29 UTC