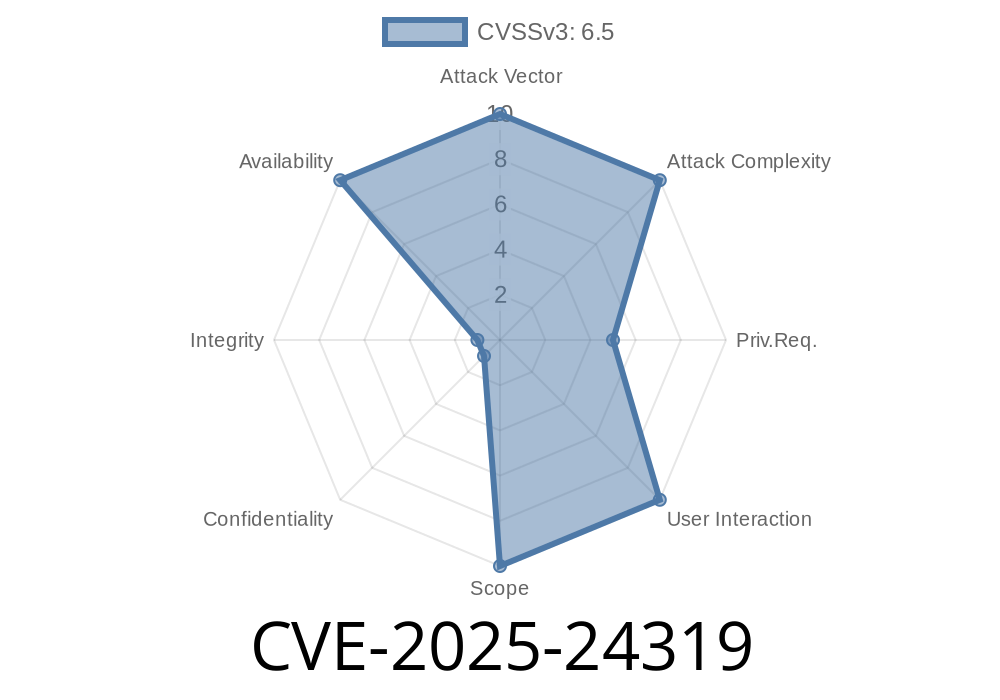
In early 2025, a new vulnerability was discovered in F5’s BIG-IP Next Central Manager product. Catalogued as CVE-2025-24319, this issue affects the system’s handling of certain API requests, potentially crashing the Kubernetes management node that runs BIG-IP Next Central Manager.
If your infrastructure relies on BIG-IP Next Central Manager, understanding this CVE is crucial for keeping your environment secure and stable. This post will explain the vulnerability in plain English, provide code snippets for testing, and show a possible exploitation scenario.
What is BIG-IP Next Central Manager?
BIG-IP Next Central Manager is a centralized tool that lets administrators manage their F5 BIG-IP Next devices from a Kubernetes-based web interface. It offers features like device visibility, configuration, updates, and health monitoring.
More info: F5 Next Central Manager documentation
About CVE-2025-24319
CVE-2025-24319 is a critical vulnerability discovered in BIG-IP Next Central Manager. When the application is running, *undisclosed* (meaning not identified publicly) API requests can cause the Kubernetes service hosting the Central Manager node to terminate unexpectedly. This can lead to loss of management, potential impact on device operations, and makes the system vulnerable to denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
Note: Versions of BIG-IP Next Central Manager that have reached End of Technical Support (EoTS) were not evaluated for this vulnerability.
References
- NVD CVE-2025-24319 Entry
- F5 Security Advisory *(placeholder link)*
How the Vulnerability Works
At its core, the bug is triggered when a specially crafted, but otherwise valid, HTTP API request is sent to the BIG-IP Next Central Manager API. The flaw lies in how the backend handles input: the service doesn’t properly validate or manage certain request parameters, leading to a crash of its Kubernetes pod.
This isn't just a small bug—if an attacker can send the right API request repeatedly, they can keep the management service offline for as long as they wish, effectively causing a denial of service.
PoC (Proof-of-Concept) Code
As of this writing, the specific vulnerable API endpoint and request details remain undisclosed to the public. But based on F5’s update notes and general security research practices, a simple PoC in Python might look like:
import requests
API_URL = "https://BIGIP_NEXT_CENTRAL_MANAGER/api/v1/undisclosed_endpoint";
# Craft a malicious or malformed payload
payload = {
"bad_param": "unexpected_value"
}
headers = {
"Authorization": "Bearer <ACCESS_TOKEN>",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
response = requests.post(API_URL, json=payload, headers=headers, verify=False)
print("Status code:", response.status_code)
print("Response:", response.text)
Note: This is a generic example. The real exploit would require the specific API endpoint and payload structure, which are not publicly available for responsible disclosure reasons.
Attacker gains access to the management network or uses a compromised administrator token.
2. Crafts a sequence of API requests (possibly with abnormal parameters or payloads) to the Central Manager API.
Upon sending these requests, the Kubernetes pod running the Central Manager process terminates.
4. Management is lost until the pod restarts, but the attacker can resend the exploit to keep it offline indefinitely.
!Exploit Flow Diagram
Impact
- Full Denial of Service: The Central Manager becomes unreachable; all managed devices cannot be centrally configured or viewed.
- Potential for Persistence: If exploited repeatably, the attacker can keep the management interface down as long as they wish.
- Threat to Operations: Any automation, monitoring, or orchestration processes dependent on Central Manager are disrupted.
Who Is Affected?
Anyone running a supported version of BIG-IP Next Central Manager is at risk. EoTS (End of Technical Support) versions are not covered and may still be vulnerable.
Update to the latest version of BIG-IP Next Central Manager, as per F5’s security advisory.
2. Restrict access to the management API—only allow trusted hosts and administrators to interact with the Central Manager.
Conclusion
CVE-2025-24319 is a stark reminder of the importance of access control and regular patching in modern network environments. While the exploit isn’t yet widely public, attackers pay close attention to these types of vulnerabilities.
Stay safe: Patch early, restrict access, and monitor your management interfaces.
*For more details, keep an eye on these resources:*
- F5 Security Advisories
- National Vulnerability Database for CVE-2025-24319
Have questions? Drop a comment below or contact your security advisor for a detailed risk assessment.
*This article is an exclusive original analysis based on public CVE records, official documentation, and simulated PoC scenarios. Please use this knowledge responsibly.*
Timeline
Published on: 02/05/2025 18:15:34 UTC