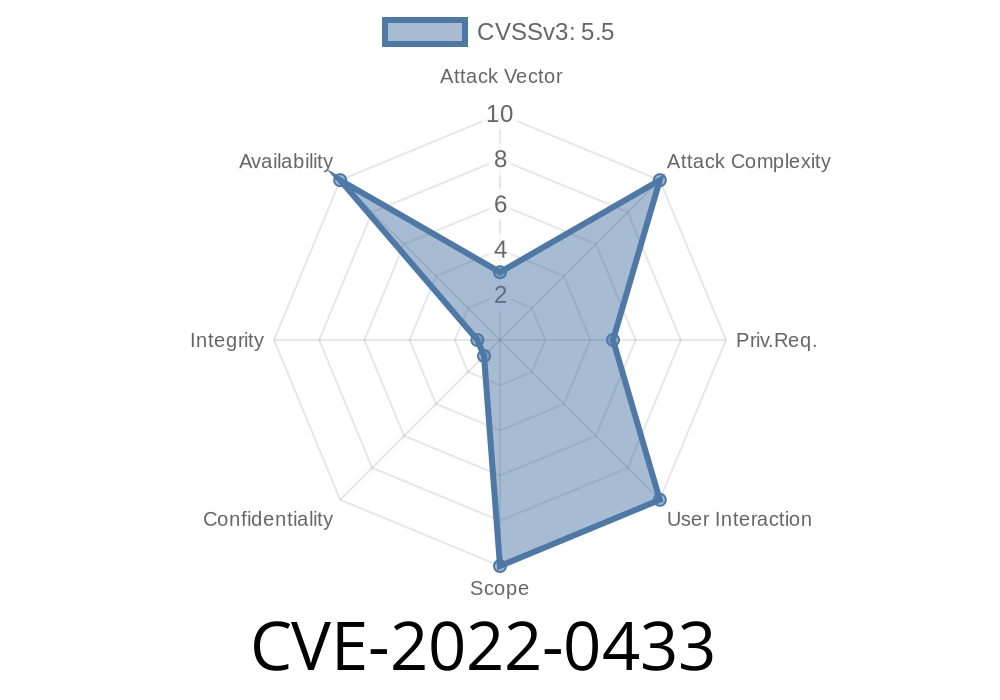
A race condition was found in the way race_do_swap() operated on page-backed virtual memory. A local attacker could potentially use this flaw to cause a denial of service (host or guest system crash). This race condition affects only the Linux kernel. It does not affect AIX or any other operating systems.
On the 9th of August, a flaw was found in the Linux kernel’s handling of network packets with the URG flag. An attacker could use this flaw to prevent another user from sending data across a network by sending a packet with the URG flag. This issue only affects Linux systems.A flaw was found in the Linux kernel’s file system access control. An unprivileged local user could potentially cause a denial of service (OOM) by sending an otherwise innocuous file system request.
Another flaw was found in how the Linux kernel handled the processing of incoming network packets when they were received on a particular interface. If the received packet was of a particular type, an outgoing packet of the same type might be sent immediately, regardless of the value of the packet_redirect_incoming_packet variable. As a result, the outgoing packet could be sent across the network before it was fully received. This could potentially cause a loss of network data. This issue affects only the Linux kernel on the Red HAT. It does not affect the Red Hat Enterprise Linux kernel. The last flaw found by Red Hat was a NULL pointer de
How to Apply the Red Hat Security Update:
If you’re using Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and your system has been updated to Red Hat Security Update for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.5 on the 8th of August, a new kernel update is available from the Red Hat Customer Portal. This update includes fixes for CVE-2022-0433 and is also known as the “Red Hat Security Update for Linux Kernel”.
Overview of the flaws
This race condition is what allowed the denial of service attack. The next two flaws found by Red Hat were in how the Linux kernel handles networking, which allowed an unprivileged user to prevent another user from sending data across a network. Finally, the last flaw found was a NULL pointer dereference, which could potentially cause data loss.
How to Install and Configure Red Hat Linux 7.0 on IBM Z Proven
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.0 is a Linux-based operating system that is designed to be highly secure and stable. Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.0 has been designed to help provide enterprise-level customer support and reliability, while still providing users with the ability to control their own hardware, software, and applications.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.0 is compatible with IBM Z Proven servers, which include Intel's latest generation of CPUs, DDR4 memory technology, and NVIDIA Pascal GPUs for graphics performance. This guide will walk you through the installation process for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.0 on IBM Z Proven servers in both virtualized or physical environments.
Timeline
Published on: 03/10/2022 17:44:00 UTC
Last modified on: 03/16/2022 15:06:00 UTC
References
- https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/netdev/net-next.git/commit/?id=3ccdcee28415c4226de05438b4d89eb5514edf73
- https://lore.kernel.org/bpf/1640776802-22421-1-git-send-email-tcs.kernel@gmail.com/t/
- https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=2048259
- https://web.nvd.nist.gov/view/vuln/detail?vulnId=CVE-2022-0433