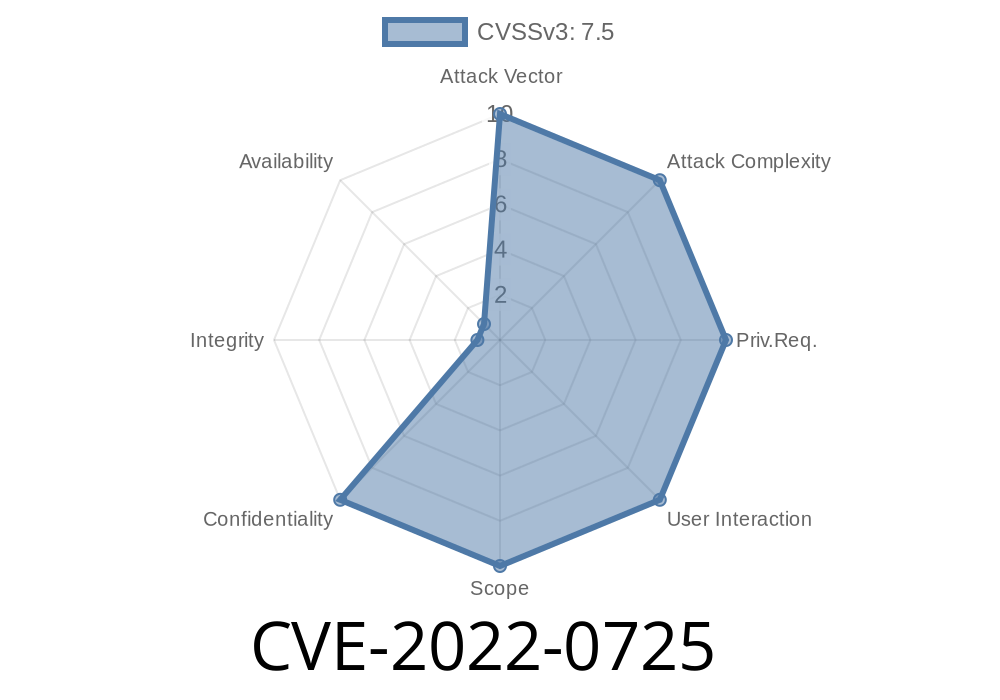
An attacker can use the information to break into the KeePass database and gain access to the system. This can be done by tricking KeePass into logging the password in the system log and then using the information to access the database. A successful exploit against this issue results in unauthorized access to the KeePass database.
There are no workarounds available to mitigate this issue. However, KeePass users should ensure that the system is not logging password information in the system log.
This issue was resolved by upgrading KeePass to version 2.3.11.
A security issue was found in KeePass. Malicious users can use this issue to execute remote code on the system.
In case you are using a remote http server like mongodb, you can use a tool like nginx to reverse proxy the requests to the remote server. An attacker can use the information to carry out a variety of attacks.
An unauthenticated user can exploit this issue to execute remote code on the system. By default, KeePass does not contain any code to validate the X.509 certificate of the HTTP server. An attacker can exploit this issue to trick the KeePass database into accepting an invalid X.509 certificate and then carry out a man-in-the-middle attack to carry out a wide range of attacks on the system.
This issue was resolved by upgrading KeePass to version 2.1.15.
A vulnerability was found in KeePass.
Summary of vulnerability
In case you are using a remote http server like mongodb, you can use a tool like nginx to reverse proxy the requests to the remote server. An attacker can use the information to carry out a variety of attacks.
An unauthenticated user can exploit this issue to execute remote code on the system. By default, KeePass does not contain any code to validate the X.509 certificate of the HTTP server. An attacker can exploit this issue to trick the KeePass database into accepting an invalid X.509 certificate and then carry out a man-in-the-middle attack to carry out a wide range of attacks on the system.
This issue was resolved by upgrading KeePass to version 2.1.15
Vulnerability Details
A remote code execution vulnerability in KeePass was discovered and fixed.
When using a remote HTTP server like mongodb, you can use a tool like nginx to reverse proxy the requests to the remote server. An attacker can exploit this issue to carry out a wide range of attacks on the system.
Description of the KeePass Vulnerability
KeePass is a password manager that can be used to create, store, and manage passwords for websites.
A vulnerability in the application allowed an unauthenticated user to execute remote code on the system. This issue was resolved by upgrading the application to version 2.1.15.
Authorization issue :
An attacker can exploit this issue to execute remote code on the system. By default, KeePass does not contain any code to validate the X.509 certificate of the HTTP server. An attacker can exploit this issue to trick the KeePass database into accepting an invalid X.509 certificate and then carry out a man-in-the-middle attack to carry out a wide range of attacks on the system.
This issue was resolved by upgrading KeePass to version 2.1.15.
Timeline
Published on: 03/10/2022 17:44:00 UTC
Last modified on: 06/14/2022 14:38:00 UTC