This vulnerability affects Windows client and server operating systems. It can be exploited by malicious users to install arbitrary code in vulnerable computers. This attack can be reliably performed only if the target computer is running Windows. However, Google Project Zero researchers have discovered several vulnerabilities in certain versions of Windows and MacOS that can be exploited by malicious hackers. Moreover, these vulnerabilities can also be exploited via Remote Desktop Protocol and X11, as well as other protocols. Please note that the majority of MacOS and Linux distributions are not vulnerable to this issue. However, there are some Linux distributions that might be affected. For example, the Debian and YUM package managers are not vulnerable to this issue. However, the Linux distributions that use the Red Hat Package Manager might be affected.
What is Cross-Site Scripting?
Cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks are a type of security vulnerability that allow hackers to inject malicious scripts into web pages. This allows them to steal user credentials, inject malware into the target's browser, or perform other actions.
This vulnerability affects most browsers running on Microsoft Windows, as well as Internet Explorer for Windows and Mac OS X.
Description of the Vulnerability
This vulnerability affects Windows client and server operating systems. It can be exploited by malicious users to install arbitrary code in vulnerable computers. This attack can be reliably performed only if the target computer is running Windows. However, Google Project Zero researchers have discovered several vulnerabilities in certain versions of Windows and MacOS that can be exploited by malicious hackers. Furthermore, these vulnerabilities can also be exploited via Remote Desktop Protocol and X11, as well as other protocols.
How Did This Vulnerability Get Discovered?
In September 2018, Google Project Zero researchers discovered a vulnerability in the Windows and MacOS operating systems that allows for arbitrary code to be installed on vulnerable computers. This is because certain versions of Windows and MacOS are vulnerable to this attack. Microsoft has released an update for this issue on October 24, 2018, which fixes the problem. The exploitability of this vulnerability can be mitigated if users have updated their systems. The most recent version of the Linux Kernel that is currently available at the time of writing is 4.18, but it is still not immune to exploitations of this bug.
Microsoft Windows software vulnerability
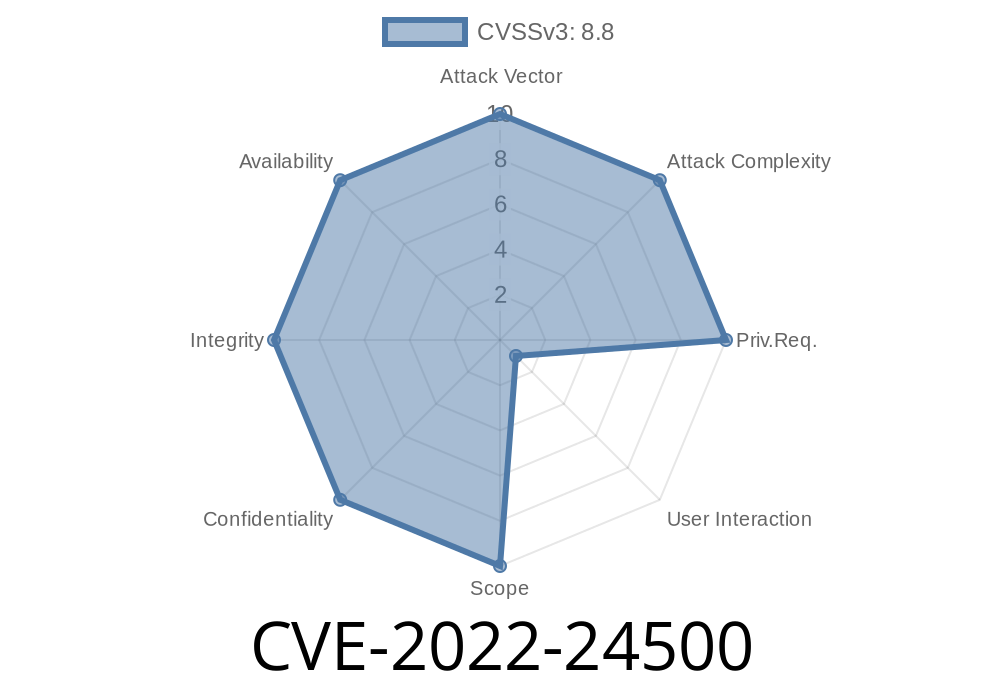
A vulnerability that affects Microsoft Windows client and server operating systems has been discovered by Google Project Zero team. This vulnerability is known as CVE-2022-24500 and it was disclosed on February 21, 2019.
According to the researcher who discovered this vulnerability, it is a privilege escalation flaw that can be exploited via Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) or X11 protocol. The attacker can exploit this flaw to install arbitrary code in vulnerable computers.
Furthermore, this attack can be reliably performed only if the target computer is running Windows. However, other operating systems such as MacOS, Linux, and others are not vulnerable to this issue.
Timeline
Published on: 04/15/2022 19:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 04/22/2022 15:54:00 UTC