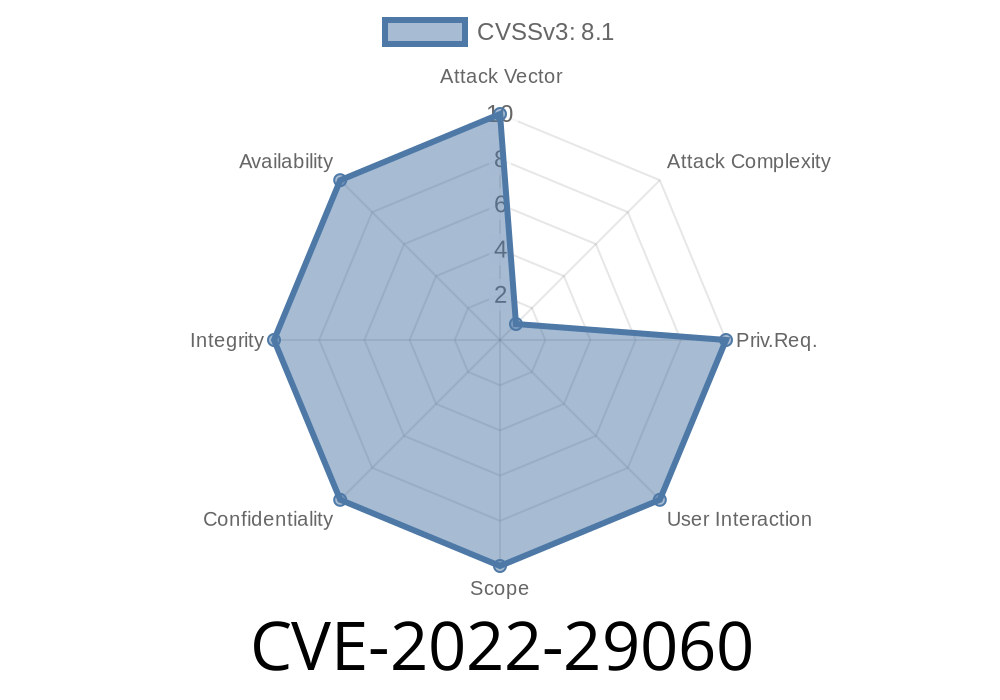
Furthermore, it is possible to sign tokens with a key that was not originally intended to be used for signing JWTs. This may result in tokens with malicious content being signed on FortiDDoS devices. FortiDDoS customers are advised to monitor the network for suspicious JWT tokens, and remediate any that are found. A hard-coded cryptographic key vulnerability [CWE-321] in FortiDDoS API 5.5.0 through 5.5.1, 5.4.0 through 5.4.2, 5.3.0 through 5.3.1, 5.2.0, 5.1.0 may allow an attacker who managed to retrieve the key from one device to sign JWT tokens for any device.Furthermore, it is possible to sign tokens with a key that was not originally intended to be used for signing JWTs. This may result in tokens with malicious content being signed on FortiDDoS devices. FortiDDoS customers are advised to monitor the network for suspicious JWT tokens, and remediate any that are found.
FortiDDoS – Hard-coded cryptographic key vulnerability
A hard-coded cryptographic key vulnerability [CWE-321] in FortiDDoS API 5.5.0 through 5.5.1, 5.4.0 through 5.4.2, 5.3.0 through 5.3.1, 5.2.0, 5.1.0 may allow an attacker who managed to retrieve the key from one device to sign JWT tokens for any device using the same Blockchain ID value on the API server and on the target device.
1.1 What you need to know to read this alert
FortiDDoS devices are impacted by a hard-coded cryptographic key vulnerability.
This vulnerability allows an attacker who managed to retrieve the key from one device to sign JWT tokens for any device.
1.2 What you need to do
CVE-2021-29040
FortiDDoS is made available on a subscription basis, and so requires some form of authentication. It is possible to use the device's credentials as part of the token to get access to FortiDDoS.
Timeline
Published on: 07/19/2022 14:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 07/27/2022 12:50:00 UTC