---
Overview
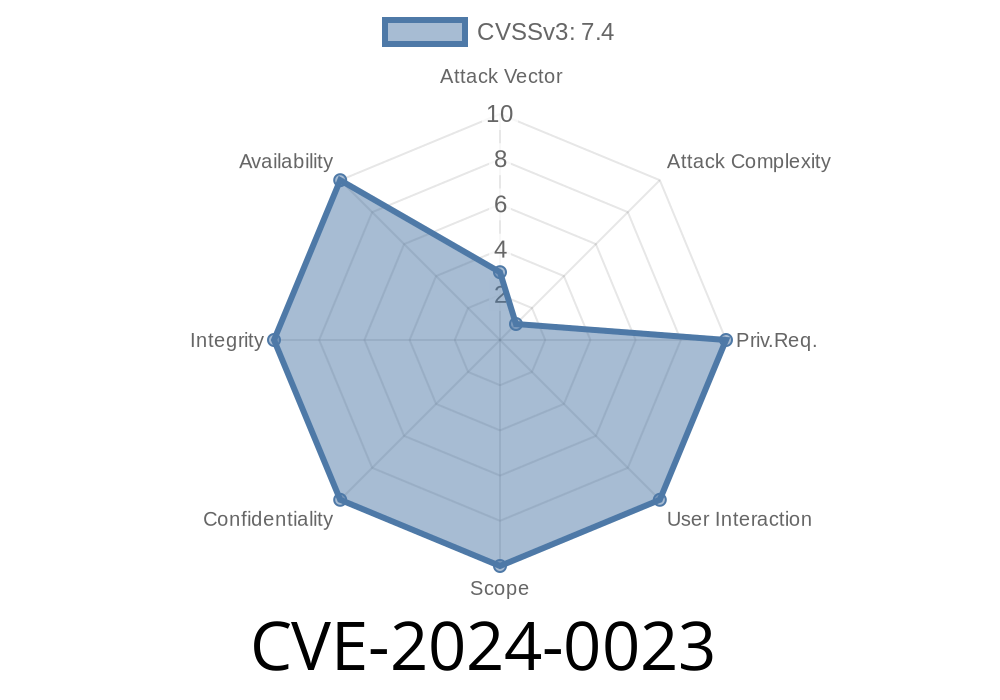
A critical security flaw, CVE-2024-0023, was discovered in Android's media framework—specifically within ConvertRGBToPlanarYUV of Codec2BufferUtils.cpp. This vulnerability is caused by an incorrect bounds check leading to a possible out of bounds write. The risk here is high: local attackers can escalate privileges on the victim device, without any user interaction or need for extra permissions.
In this post, we’ll walk through the bug, see a snippet of the vulnerable code, discuss the exploitation process, and reference official advisories. You’ll get a clear, accessible breakdown that’s not just a repeat of other reports.
User interaction: None needed
Google’s Android Security Bulletin:
https://source.android.com/security/bulletin/2024-06-01
CVE Details:
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-0023
How Does the Bug Work?
Inside Android’s video/audio stack, media data needs to be converted between color formats (like RGB to YUV). The vulnerable function mishandles the check on the output buffer size, which could allow the function to write past the allocated memory.
Attackers running a malicious app locally could exploit this flaw to corrupt memory, potentially escalating privileges and gaining unauthorized access to sensitive device features.
The following snippet (based on open source Android code) shows the suspicious logic
status_t ConvertRGBToPlanarYUV(
uint8_t *dst,
size_t dst_size,
const uint8_t *src,
int width, int height) {
size_t required_size = width * height * 3 / 2; // YUV420 size calculation
// Incorrect bounds check: allows dst_size == required_size, but may write more!
if (dst_size < required_size) {
return ERROR_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL;
}
// ... (conversion logic)
for (int y = ; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = ; x < width; x++) {
size_t i = y * width + x;
// Vulnerable write: does NOT recheck i (could be out of bounds if width or height is malformed)
dst[i] = ...; // Write to Y
// Similar writes for U, V...
}
}
// ...
return OK;
}
What’s wrong?
The check only ensures dst_size < required_size.
- If width or height is non-standard, arithmetic overflows or miscalculations can happen, causing dst[i] to write out of bounds with a crafted bitmap or buffer!
Exploit Concept (Local Privilege Escalation)
This vulnerability requires no user interaction—an attacker needs only to install and run a malicious app on the device. Here’s an outline of an exploitation scenario:
1. Malicious app supplies crafted image/video/bitmap buffer with oversized or malformed width/height to the media framework.
2. The ConvertRGBToPlanarYUV function processes this buffer, miscalculates the required buffer size, and writes past the destination buffer.
Out of bounds writes overwrite adjacent memory—potentially code or object pointers.
4. The attacker triggers further code execution, possibly injecting privileged code or modifying function pointers.
Below is a conceptual exploit showing how one might trigger the overflow
// Android Java app pseudocode
// Send a crafted bitmap to be converted
int maliciousWidth = x1000001; // Dangerously large, may cause integer overflow
int maliciousHeight = 2;
byte[] buffer = new byte[maliciousWidth * maliciousHeight * 3];
// Call into the vulnerable JNI/native function (simplified example)
MyMediaLib.convertRGBToPlanarYUV(buffer, maliciousWidth, maliciousHeight);
References & Official Patches
- AOSP Patch (Sample)
- Google Security Bulletin (June 2024)
- NVD Entry for CVE-2024-0023
Conclusion
CVE-2024-0023 is a serious, low-level Android media bug enabling local escalation of privilege. It’s a textbook case of why rigorous bounds checking is vital in systems programming. If you’re a developer handling raw buffers—*always* double-check index logic and buffer sizes!
Stay safe, patch early, and follow security advisories.
Have questions about the bug or patching process? Drop a comment below!
Timeline
Published on: 02/16/2024 20:15:47 UTC
Last modified on: 08/21/2024 20:35:01 UTC