Microsoft Edge, the browser built on Chromium, is widely known for blending speed with safety. But even the most secure platforms can have weak spots. Recently, CVE-2024-26246 emerged—an alarming security feature bypass vulnerability targeting Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based). In this article, I’ll break down what CVE-2024-26246 means in plain English, show how it works, and highlight why it matters for everyday users and security professionals.
What is CVE-2024-26246?
CVE-2024-26246 is a security feature bypass discovered in Microsoft Edge’s Chromium-based platform. In security terms, a “feature bypass” means an attacker can sidestep built-in protections without triggering usual alarms. Microsoft officially described this as:
> "A security feature bypass vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) improperly handles specific situations, allowing the bypass of certain security constraints."
> —Microsoft Security Update Guide (MSRC)
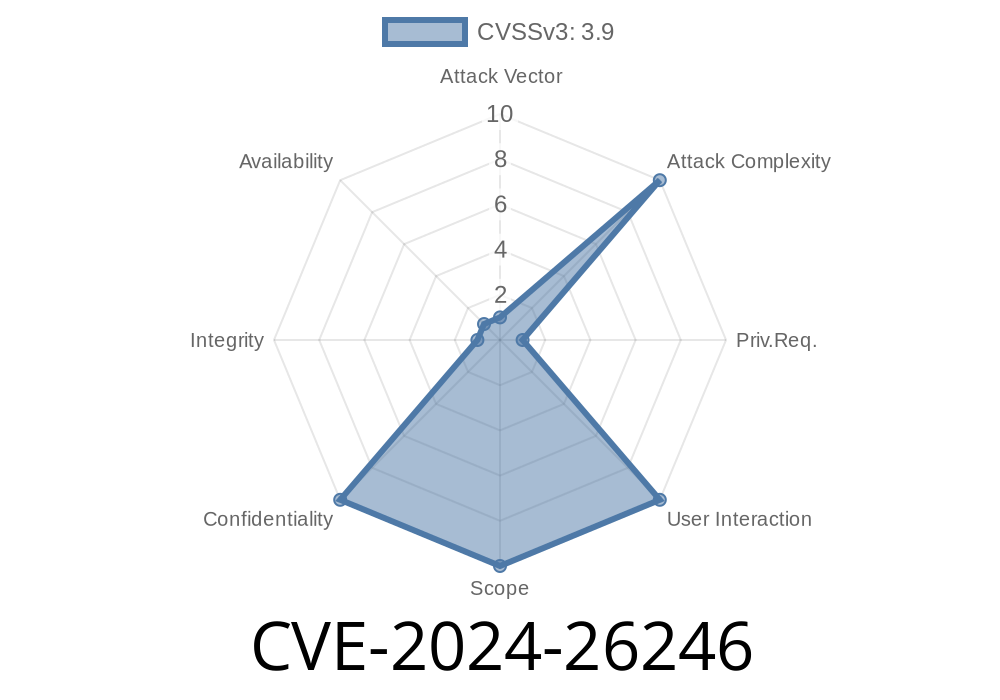
How Bad is It?
This vulnerability is significant because it could let attackers evade some browser protections that are meant to prevent malicious scripts or unsafe actions. This makes attacks like cross-site scripting (XSS), clickjacking, or other web-based threats easier.
According to Microsoft’s official note:
How Does the Exploit Work?
> Disclaimer: The following is for educational purposes only and aims to help users and IT professionals understand the risks and patch affected systems.
At its core, CVE-2024-26246’s exploit relies on the browser mishandling certain features that are supposed to block dangerous behavior—such as third-party iframes ignoring Content Security Policy (CSP), or enhanced isolation mechanisms being bypassed.
Attacker creates a malicious website that embeds a sensitive or bank-related page in an iframe.
2. Microsoft Edge fails to enforce critical protections (such as Same-Origin Policy or CSP) because of the flaw.
3. The malicious site can now interact with the embedded content or trick users into revealing credentials, clicking fake buttons, etc.
Simplified Exploit Code Snippet
Here’s an easy-to-understand code sample demonstrating how an attacker might try to bypass CSP and trick Edge:
<!-- Malicious page created by attacker -->
<iframe src="https://bank-website.com/login"; sandbox="allow-scripts allow-forms"></iframe>
<script>
// Try to interact with the iframe, which should not be possible if protections work
document.querySelector('iframe').contentWindow.postMessage('steal-creds', '*');
</script>
Without proper security enforcement, Edge might have allowed unsafe interaction, letting attackers inject scripts or steal data. Normally, this shouldn’t happen due to security policies, but CVE-2024-26246 weakens these defenses.
Everyday users: Just visiting a compromised website could expose you.
- Enterprise environments: Attackers could use this to escalate phishing or credential theft inside organizations.
- Developers/security teams: You may need to update CSP rules and review web content for unexpected behavior.
How to Stay Safe
1. Update Your Browser!
The most important fix is to update Microsoft Edge to the latest version (at least 122..2365.92).
> How-to: Go to Edge menu → Help and feedback → About Microsoft Edge.
2. Check Your Security Policies
If you’re a developer or admin, double-check your web apps’ CSP headers and iframe usage.
3. Stay Informed
Review Microsoft’s official update and release notes:
- Microsoft Security Update Guide
- Edge Release Notes
Technical Details (For Advanced Users)
The exact technical vector hasn’t been fully disclosed by Microsoft for safety, but credible sources note it likely involves improper enforcement of security contexts when loading web content or handling iframes under certain flags.
Based on Chromium’s patch logs (search for recent CSP and frame policy updates), the underlying bug may look like:
// Edge should block this, but CVE-2024-26246 caused protection failure
document.querySelector('iframe').contentWindow.eval('alert("hacked!");');
Conclusion
CVE-2024-26246 shows that even the latest browsers can be vulnerable to clever bypass tricks. The good news? Microsoft reacted quickly, and updating your browser is usually enough to protect yourself. Security is a shared responsibility—always keep your software up-to-date and be cautious of suspicious websites.
Key References
- CVE-2024-26246 on Microsoft
- Edge Security Updates
- Chromium Security Advisories
Timeline
Published on: 03/14/2024 23:15:46 UTC
Last modified on: 03/19/2024 17:05:45 UTC