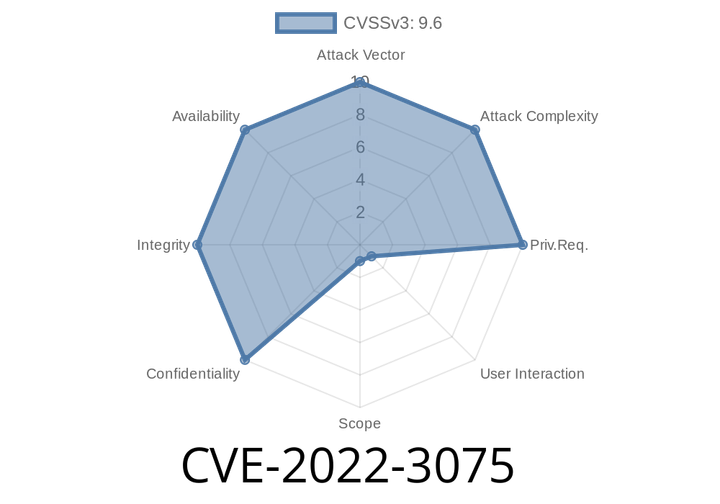
CVE-2022-3075 - A Look Into Chrome’s Mojo Sandbox Escape (with Exploit Details)
Google Chrome is considered one of the most secure web browsers in use today, but its massive codebase sometimes leaves room for dangerous security bugs.
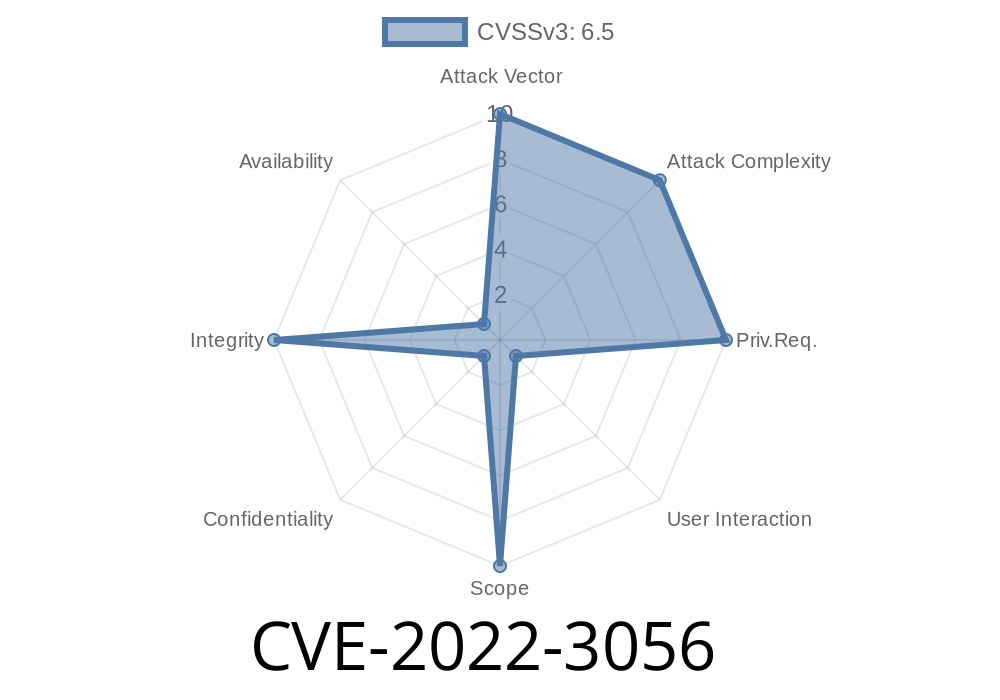
CVE-2022-3056 In prior versions of Chrome, insufficient policy enforcement allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy.
This issue has been fixed.
19 CVE-2018-4944 284 Bypass of Content Security Policy via Stored XSS In Chrome prior to version 77, if a page
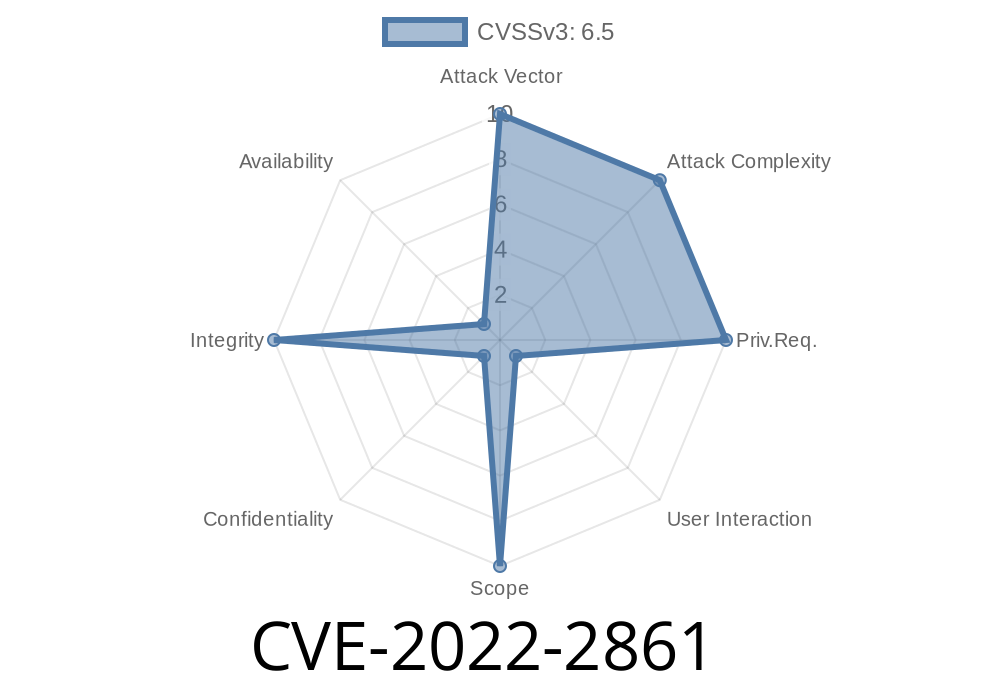
CVE-2022-2861 The Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.101 allowed attackers to inject scripts into WebUI.
An attacker could use this to inject content into WebUI, such as a phishing form, or execute arbitrary code. Google Chrome prior to 105.0.
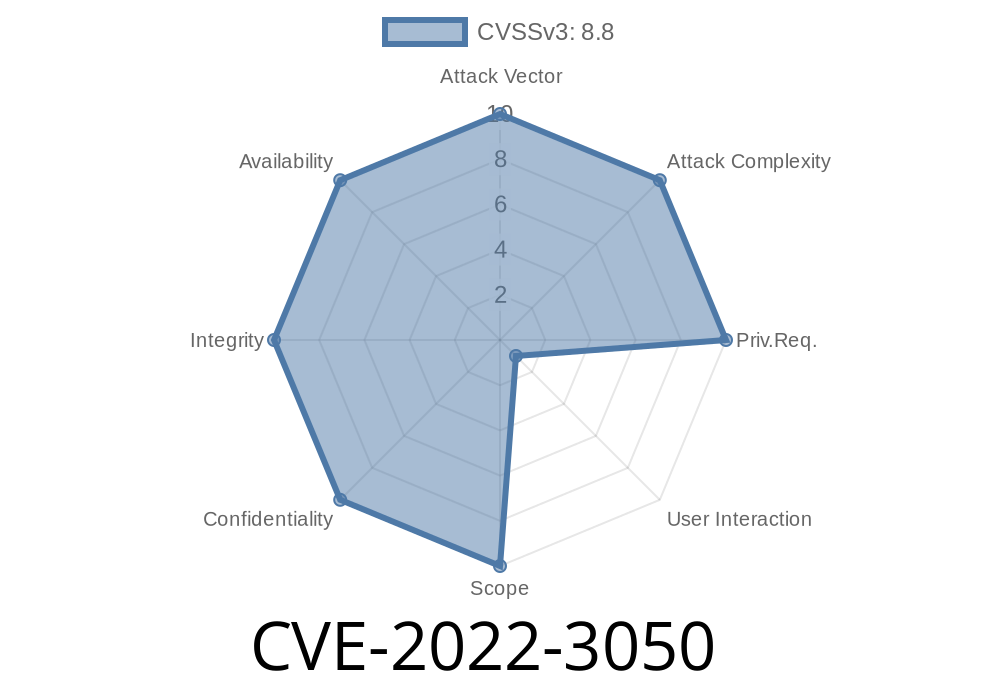
CVE-2022-3050 Heap buffer overflow in WebUI in Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to exploit heap corruption.
CVE-2018-5602 has been assigned to this issue. Google confirmed this vulnerability was limited to privileged users who had full control of the browser, rather than
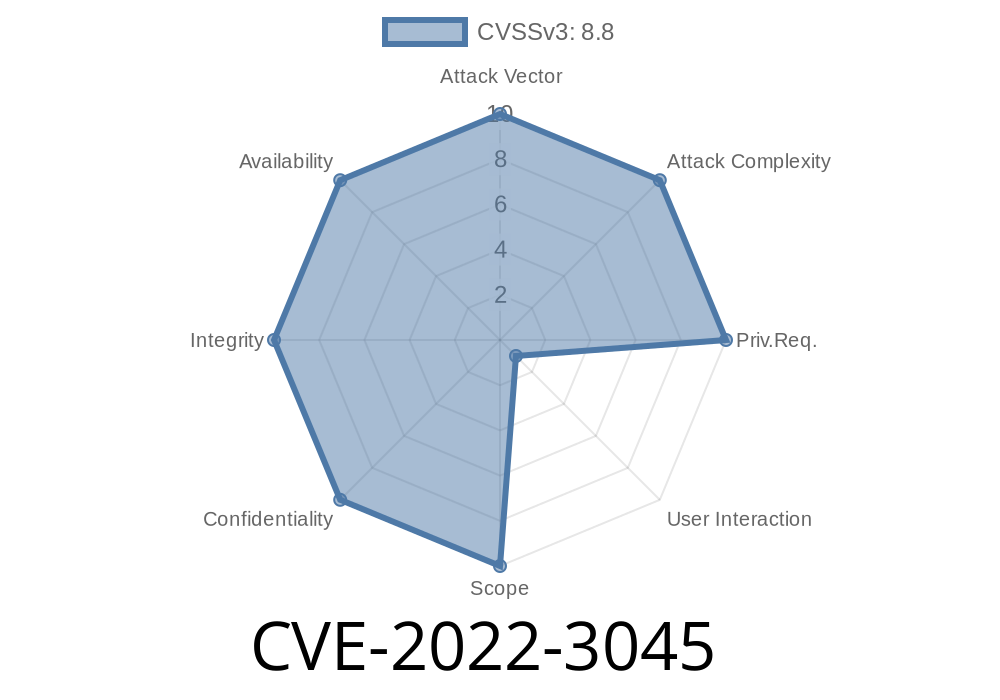
CVE-2022-3045 V8's validation of untrusted input was insufficient in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.52. This could lead to heap corruption.
CVE-2018-6063: A remote code execution vulnerability in Blink/Webkit components was fixed in V8 in Google Chrome OS prior to 69.0.3497.81. The
Episode
00:00:00
00:00:00