An address bar spoofing issue was patched in Safari. The spoofing issue allowed a remote attacker to change the destination site by injecting malicious code into a website. An information disclosure in PDF viewer was fixed. An attacker may now use this issue to reveal information about the user. An out-of-bounds read issue was patched in WebView. An attacker may now inject arbitrary code into otherwise inaccessible objects. An arbitrary code execution issue was patched in iOS. This issue may allow a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code on the system. An issue where a maliciously crafted PDF could cause information disclosure was patched in iOS. An attacker may now use this issue to reveal information about the user. A type confusion issue was patched in WebKit. This may lead to information disclosure. An issue where a maliciously crafted PDF could cause arbitrary code execution was patched in iOS. An attacker may now use this issue to execute arbitrary code on the target device. An arbitrary code execution issue was patched in macOS. This issue may allow a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code on the system. An arbitrary code execution issue was patched in watchOS. An attacker may now use this issue to execute arbitrary code on the target device. A type confusion issue was patched in iOS. This may lead to information disclosure. An arbitrary code execution issue was patched in macOS. An attacker may now use this issue to execute arbitrary code on the target device
Other Software Provided By Apple Inc .
Apple Inc. has provided the following other software to help protect your Mac. Safari Update: Fixes an address bar spoofing issue that could allow a remote attacker to change the destination site by injecting malicious code into a website. This update also fixes an information disclosure in PDF viewer that may now be used by attackers to obtain information about the user. An out-of-bounds read issue was fixed in WebView on macOS. An attacker may now use this issue to inject arbitrary code into otherwise inaccessible objects. An arbitrary code execution issue was fixed in WebKit and WebKitSandboxedProcess on macOS, which may allow a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code on the system. An arbitrary code execution issue was fixed in watchOS, which may allow a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code on the target device. Type confusion issues were fixed in iOS and watchOS that may lead to information disclosure and/or possible data loss or access by unauthorized users. A type confusion issue was fixed in Safari on macOS that may lead to information disclosure and/or possible data loss or access by unauthorized users. An issue where a maliciously crafted PDF could cause information disclosure was patched in iOS, which may now be used by attackers to obtain information about the user or perform privilege escalation attacks via physical access of the mobile device when it is unlocked with a passcode or Touch ID authentication prompt.
What is the state of web browsers today?
Web browsers are in a state of flux today. They are constantly updating and adding new features, which allows for more innovation. In addition, the increase in the number of vulnerabilities that exist on the internet means that web browsers have to keep up with maintaining security and keeping users safe. Because of this, web browsers are constantly changing, but they remain one of the most important tools in any marketing plan.
Timeline
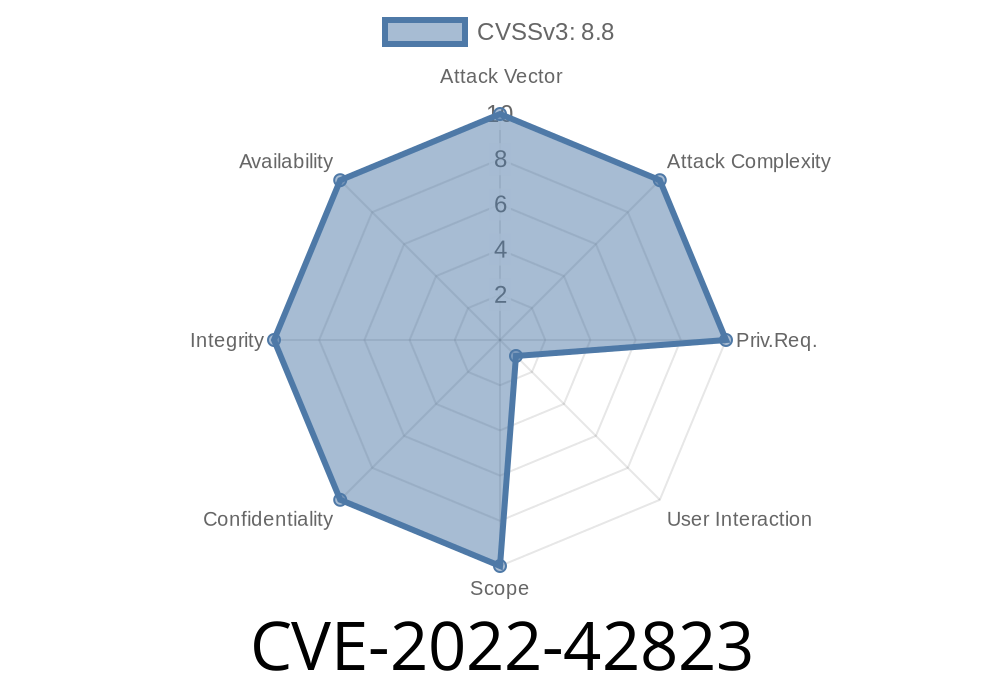
Published on: 11/01/2022 20:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 11/15/2022 03:15:00 UTC
References
- https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT213488
- https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT213495
- https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT213492
- https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT213491
- https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT213489
- http://www.openwall.com/lists/oss-security/2022/11/04/4
- https://lists.fedoraproject.org/archives/list/package-announce@lists.fedoraproject.org/message/5LF4LYP725XZ7RWOPFUV6DGPN4Q5DUU4/
- https://www.debian.org/security/2022/dsa-5274
- https://www.debian.org/security/2022/dsa-5273
- https://lists.debian.org/debian-lts-announce/2022/11/msg00010.html
- https://lists.fedoraproject.org/archives/list/package-announce@lists.fedoraproject.org/message/AQKLEGJK3LHAKUQOLBHNR2DI3IUGLLTY/
- https://lists.fedoraproject.org/archives/list/package-announce@lists.fedoraproject.org/message/JOFKX6BUEJFECSVFV6P5INQCOYQBB4NZ/
- https://web.nvd.nist.gov/view/vuln/detail?vulnId=CVE-2022-42823